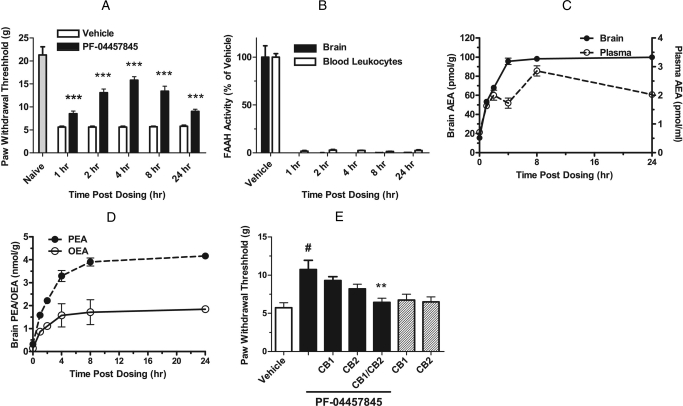
Fig. 8.
Time course for antihyperalgesic effects of PF-04457845 (1 mg/kg p.o.) in the CFA model of inflammatory pain in rats. All data are expressed as means ± S.E.M. A, a single dose treatment of PF-04457845 (1 mg/kg p.o.) produces a reduction of mechanical allodynia at least for 24 h. ***, p < 0.001; n = 11 rats per group. B to D, at 1, 2, 4, 8, and 24 h after treatment with PF-04457845, near-complete inhibition of FAAH activity (B), elevated AEA levels in brain tissue and blood leukocytes/plasma (C), and elevated PEA/OEA levels in brain tissue (D) are found. All FAAH activity and NAE measurements were determined at the indicated times after drug treatment and were significantly different between PF-04457845- and vehicle-treated groups (p < 0.001; n = 3 rats/group). E, blockade of antihyperalgesic effects of PF-04457845 (3 mg/kg p.o.) by CB1 and CB2 antagonists (SR141716 and SR144528, respectively; 3 mg/kg i.p.; each administered 10 min before measurement of PWTs). Note that neither the CB1 nor CB2 antagonist displayed significant effects on mechanical allodynia in rats not treated with PF-04457845 (hatched bars). #, p < 0.01, for PF-04457845- versus vehicle-treated groups. **, p < 0.01, for vehicle-PF-04457845 versus CB1/CB2 antagonist-PF-04457845-treated groups. n = 8 rats/group.