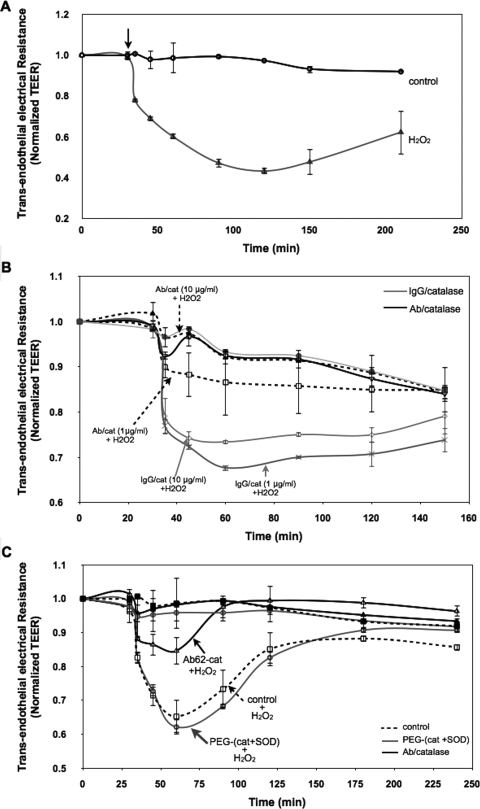
Fig. 1.
Anti-PECAM/catalase conjugates protect against endothelial barrier dysfunction induced by H2O2 insult. A, TEER across HUVEC monolayers was used to evaluate endothelial permeability. HUVEC monolayers grown onto Transwell inserts (3.0-μm pore size) were transferred to Endohm (World Precision Instruments) chambers for resistance measurement at different time points. At the arrow-indicated time point, the cells were stimulated with H2O2 (400 μM). The recorded values were normalized to the initial resistances of the monolayers before H2O2 treatment. The normalized TEER values are represented as means ± S.D. (n = 3). B, Ab/catalase treatment (1 and 10 μg/ml) abolished H2O2-induced endothelial hyperpermeability. HUVEC monolayers were preincubated with conjugates for 30 min and washed three times to remove unbound conjugates. Cells then were stimulated with H2O2 (400 μM) and subjected to TEER measurement. C, mixture of PEGylated SOD and catalase (10 μg/ml of each) failed to attenuate H2O2-induced TEER decline.