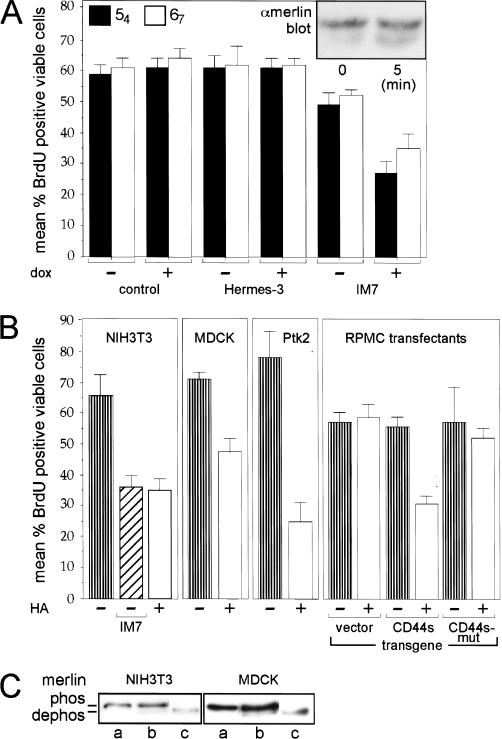
Figure 6.
CD44-dependent merlin activation and growth inhibition in several cell lines. (A) The CD44-specific antibody IM7 activates merlin. Cells from clones 54 and 67 were seeded into 8-well chamber slides at low density. Either IM7 or Hermes-3 (control antibody) and doxycycline were added where indicated and incubated for 12 h (control cells were without antibody). Cells then were labeled with BrdU for 60 min and stained for incorporation using a biotinylated BrdU antibody. The mean percent cells that incorporated BrdU, are plotted and standard errors are indicated. The insert shows a Western blot (higher resolution gel) detecting doxycycline-induced merlin (α-merlin C-18) from lysates of clone 67 cells at low density prior (0 min) or after treatment with IM7 for 5 min. (B) CD44-dependent activation of merlin and inhibition of growth in several types of cells. All cells were seeded into 8-well chamber slides at low density and incubated with HA or IM7 where indicated, for 12 h. BrdU incorporation and detection as in A. The CD44 antibody IM7 (as well as KM81, not shown) inhibited proliferation of NIH3T3 cells similarly to the result in A. HA activated merlin in mouse fibroblasts (NIH3T3 cells), in dog kidney epithelial cells (MDCK), and rat kangaroo epithelial cells (Ptk2). In addition cells negative for CD44 when stably transfected with a construct encoding full-length CD44s but not CD44 mutated in the ERM-binding domain, were also growth-inhibited in response to HA treatment. (C) Addition of HA induces dephosphorylation of merlin in several types of cells. NIH3T3 and MDCK cells as in B were harvested untreated (a) or after treatment with 100 μg/mL of HA (b) for 12 h (similar dephosphorylation after 5 min, not shown). Cell lysates were treated with CIP (c) prior to Western blotting (higher-resolution gel) as in A.