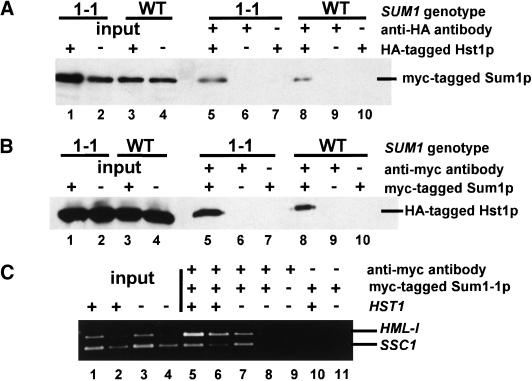
Figure 6.
Hst1p was in complexes with both Sum1-1p and wild-type Sum1p. (A) A MATα haploid of the genotype sir2Δ sum1Δ hst1Δ (JRY7151) was transformed with a plasmid expressing 3myc–Sum1-1p (pJR2291, lanes 1,2,5–7) or 3myc–Sum1p (pJR2292, lanes 3,4,8–10) and a second plasmid expressing Hst1–5HAp (pJR2289, lanes 1,3,5,7,8,10) or Hst1p (pJR2288, lanes 2,4,6,9). Transformed cells were grown in minimal medium requiring maintenance of both plasmids. A total of 1/30 of input (lanes 1–4) or 1/15 of immunoprecipitated samples (lanes 5–10) was analyzed for the presence of myc-Sum1-1p or myc-Sum1p by immunoblotting. Negative control lanes had samples prepared with an untagged version of Hst1p (lanes 6,9) or without antibody in the immunoprecipitation (lanes 7,10). (B) A MATα haploid of the genotype sir2Δ sum1Δ hst1Δ (JRY7151) was transformed with a plasmid expressing Hst1–5HAp (pJR2289, all lanes) and a second plasmid expressing 3myc–Sum1-1p (pJR2291, lanes 1,5,7), Sum1-1p (pJR2293, lanes 2,6), 3myc–Sum1p (pJR2292, lanes 3,8,10) or Sum1p (pJR2294, lanes 4,9). A total of 1/30 of input (lanes 1–4) or 1/15 of immunoprecipitated samples (lanes 5–10) was analyzed for the presence of Hst1–5HAp by immunoblotting. (C) Chromatin immunoprecipitations used MATα haploids of the genotypes sir2Δ HST1 7myc–SUM1-1 (JRY7153), sir2Δ hst1Δ 7myc–SUM1-1 (JRY7178), and sir2Δ hst1Δ SUM1-1 (JRY7157). A total of 1/23,000 (lanes 1,3) or 1/46,000 (lanes 2,4) of the input DNA or 1/25 (lanes 5,7,9–11) or 1/50 (lanes 6,8) of the immunoprecipitated DNA was analyzed.