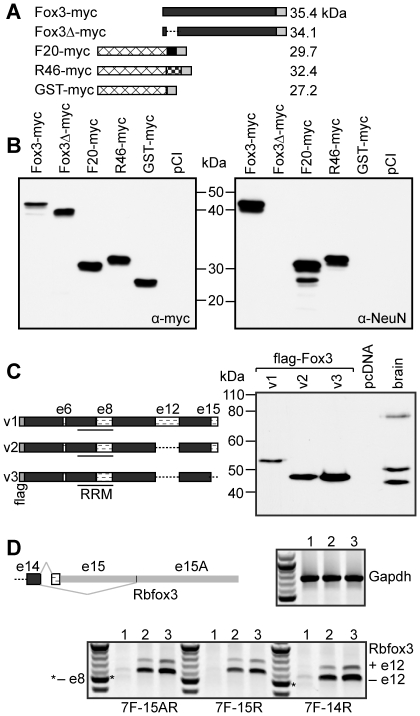
Figure 3. The anti-NeuN epitope of Rbfox3 maps to the extreme N-terminus of the protein.
A,B. The proteins depicted in A were expressed in 293T cells and analyzed by western with anti-myc-tag (left panel), or anti-NeuN antibodies on duplicate blots. Anti-NeuN recognises both F20 and R46, and amino acids 5–20 (deleted in Fox3Δ-myc) are necessary for recognition of full-length Rbfox3 by anti-NeuN. C. Three Rbfox3 splice variants were expressed in HeLa cells and compared to NeuN from mouse brain by western with anti-NeuN. Variant 1 (v1) corresponds to NP_001034256, v2 to NP_001034257, and v3 to NP_001020102. Exon numbers are as described in [13]. D. RT-PCR of total RNA from P19 cells prior to neuronal induction (lanes 1), P19 cells 7 days after neuronal induction with RA (lanes 2), and P10 mouse brain (lanes 3). For Rbfox3, 3 reverse primers were used to assess mRNAs that encode the short C-terminus (or -IGTM protein isoforms, 15A-R), the longer, -FTPY isoforms (15-R), or all mRNAs (14-R). A common forward primer to exon 7 (7-F) was used for all. Gapdh was used as a loading control.