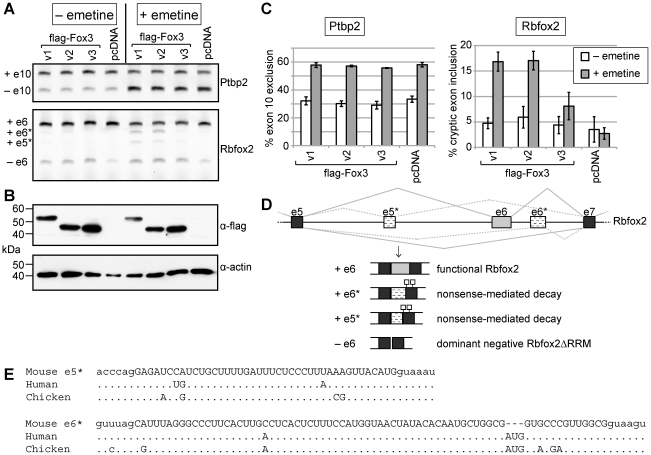
Figure 6. Rbfox3 variants enhance inclusion of cryptic exons in Rbfox2, leading to nonsense-mediated decay.
N2A cells were transiently transfected with Rbfox3 variants 1, 2 or 3 harboring N-terminal flag-tags, or pcDNA3 vector control, and treated with emetine to inhibit NMD. A. Alternative splicing of endogenous mRNAs encoding Ptbp2 and Rbfox2 was assayed by RT-PCR. Enhanced exclusion of Ptbp2 exon 10 was used as a positive control for emetine treatment. Rbfox2 spliced products are described in D. B. Western with anti-flag was used to confirm Rbfox3 overexpression; anti-actin was used as a loading control. C. Quantification of the results shown in A and 2 additional experiments (i.e. n = 3); results are displayed as average +/− standard deviation. D. Schematic representation of alternative splicing of the Rbfox2 message around exon 6, indicating the relative positions of cryptic exons 5* and 6*. The functional outcomes for the resulting spliced mRNA products are depicted below; inclusion of exon 5* or exon 6* results in the presence of 2 in-frame nonsense codons in exon 7, and destruction of these messages by nonsense-mediated decay. E. The sequences of mouse Rbfox2 exons 5* and 6* (upper case) and surrounding intronic sequence (lower case) are shown aligned to the corresponding regions from human and chicken.