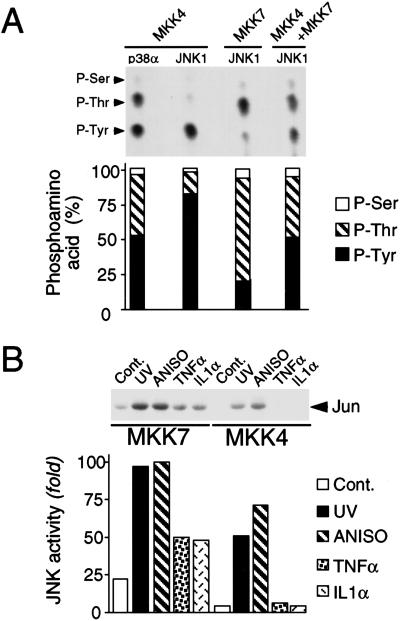
Figure 1.
Biochemical characterization of MKK4 and MKK7. (A) JNK is preferentially phosphorylated on Tyr by MKK4 and on Thr by MKK7. Epitope-tagged MKK4 and MKK7 were isolated from COS cells exposed to UV-C radiation. In vitro protein kinase assays were performed using [γ-32P]ATP and purified bacterially expressed p38α or JNK1 as substrates for MKK4 and MKK7. The phosphorylated JNK and p38α were examined by phosphoamino acid analysis and autoradiography (upper panel). The relative phosphorylation on Thr and Tyr was examined by PhosphorImager analysis (lower panel). P-Ser, phosphothreonine; P-Thr, phosphothreonine; P-Tyr, phosphotyrosine. (B) MKK4 and MKK7 are selectively activated by extracellular stimuli. Wild-type MEF were untreated (Cont.) or treated with UV-C (60 J/m2; UV) or anisomycin (1 μg/mL; ANISO) for 1 h, or with TNFα (10 ng/mL) or IL1α (15 ng/mL) for 15 min. Endogenous MKK4 and MKK7 were immunoprecipitated using an anti-rabbit polyclonal antibody to MKK4 (K18, Santa Cruz) and a goat polyclonal antibody to MKK7 (T19, Santa Cruz), respectively. MKK activity was measured in the immune complex by a coupled protein kinase assay with JNK1 and c-Jun as the substrates. Phosphorylated c-Jun was detected after SDS-PAGE by autoradiography (upper panel) and was quantitated by PhosphorImager analysis (lower panel).