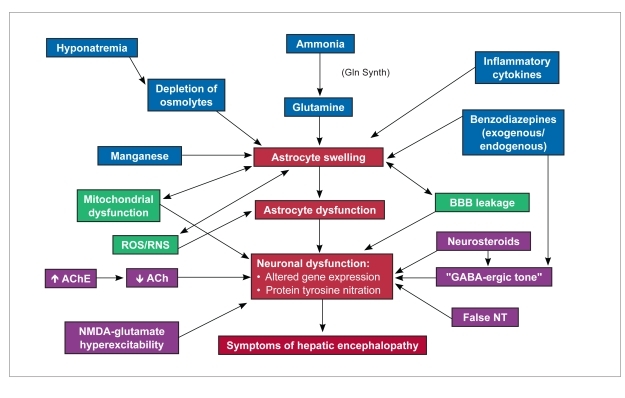
Figure 1.
Hypothesis of the multifactorial nature of hepatic encephalopathy. Various neurotoxins and NTs act independently or perhaps synergistically to cause astrocyte swelling and subsequent astrocyte dysfunction. In addition, increased “GABA-ergic tone” and depletion of Ach may contribute to neurologic dysfunction in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. A vicious cycle may perpetuate the disease, as ROS trigger astrocyte swelling, and further swelling causes production of more ROS and RNS and subsequent mitochondrial energy failure.
- Ach
- acetylcholine
- AChE
- acetylcholinesterase
- BBB
- blood brain barrier
- GABA
- gamma aminobutyric acid
- Gln Synth
- glutamine synthetase
- NMDA
- N-metyhl-D-aspartic acid
- NT
- neurotransmitter
- RNS
- reactive nitrogen species
- ROS
- reactive oxygen species