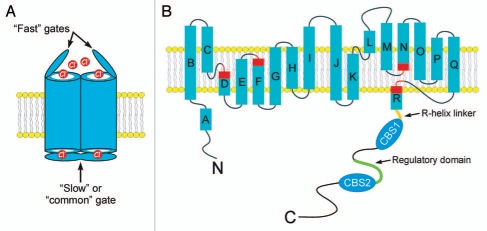
Figure 1.
(A) Cartoon showing a CLC homodimer with “fast” and “slow” or “common”gates. (B) Predicted membrane topology of a CLC monomer. Rectangles indicate α-helices. Regions of helices highlighted in red function in channel gating and to coordinate Cl− within the ion conducting pore. Note that the R-helix protrudes into the cytoplasm. In eukaryotes, the R-helix is connected to a large cytoplasmic C-terminus. A model of the CLH-3b C-terminus is shown. The C-terminus contains two cystathionine-β-synthase or CBS domains. The R-helix is connected to CBS1 via a 20 amino acid linker shown in orange. The linker between CBS1 and CBS2 is 176 amino long and contains a 101 amino acid regulatory domain shown in green. GCK-3 binds to the first four amino acids of this domain and mediates phosphorylation of two serine residues 70 and 75 amino acids downstream.