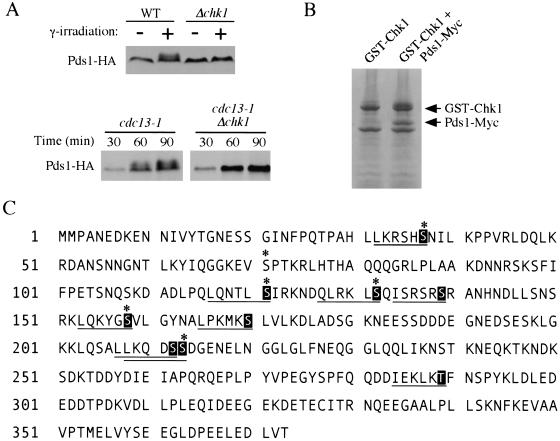
Figure 1.
Identification of the Chk1 phosphorylation sites on Pds1. (A) Chk1-dependent phosphorylation of Pds1 in response to DNA damage. Y808 (WT) and Y1071 (Δchk1) cells expressing HA-tagged Pds1 were arrested before anaphase with nocodazole (10 μg/mL) for 2 h at 30°C, then the cultures were either left untreated (−) or exposed to γ-radiation (+, 6 krad). Protein samples were prepared 45 min after irradiation and processed for Western blot analysis (top). Y809 (cdc13-1) and Y811 (cdc13-1 Δchk1) cells expressing HA-tagged Pds1 were synchronized in G1 by α-factor at 24°C and released at 32°C. Aliquots were withdrawn at indicated time to examine the Pds1-HA protein (bottom). (B) Phospho-Pds1 was purified from insect cell lysates and analyzed by mass spectrometry. Insect cells (Hi5) were coinfected with recombinant baculoviruses encoding GST-Chk1 and Pds1-Myc. GST-Chk1–Pds1 complexes were purified from cell lysates with glutathione beads and incubated with ATP. Proteins were separated on Tris-Glycine gradient gels (4–12%) and stained with coomassie blue. (C) Putative Chk1 phosphorylation sites on Pds1. Amino acid sequence of Pds1 with putative phospho-acceptor sites marked in black boxes. Chk1 phosphorylation consensus sequences are underlined. Six Ser residues mapped by mass spectrometry are marked with asterisks.