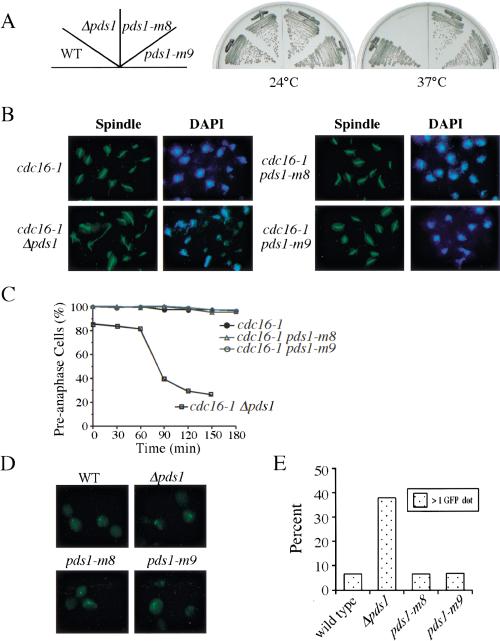
Figure 3.
Pds1-m8 and Pds1-m9 mutant proteins are functional. (A) pds1-m8 and pds1-m9 are viable at 37°C. Y300 (WT), Y175 (Δpds1), Y1072 (pds1-m8), and Y1073 (pds1-m9) were struck onto YPD plates and incubated at either 24°C or 37°C. (B,C). pds1-m8 and pds1-m9 mutants are proficient for maintaining the cdc16-1 arrest. Y1076 (cdc16-1), Y1077 (cdc16-1 Δpds1), Y1078 (cdc16-1 pds1-m8), and Y1079 (cdc16-1 pds1-m9) cells were synchronized in G1 with α-factor at 24°C and released into YPD containing 200 mM HU for 2.5 h to synchronize cells in S phase. During the last 30 min of the HU block, cells were shifted to 37°C to inactivate cdc16-1. Cells then were released from HU at 37°C. Aliquots were withdrawn at timed intervals to examine spindle morphology. Spindle morphology at 150 min for various strains are shown in B. Kinetics of anaphase entry was evaluated by the disappearance of short spindles (C). (D,E) pds1-m8 and pds1-m9 are proficient for the spindle checkpoint. Nocodazole (15 μg/mL) was added to exponentially growing cultures of Y974 (WT), Y1080 (Δpds1), Y1081 (pds1-m8), and Y1082 (pds1-m9) at 23°C. After 3 h, aliquots were withdrawn and fixed, and sister chromatids cohesion was examined. The percentage of nuclei with separated GFP signals was determined from the analysis of >100 cells (E).