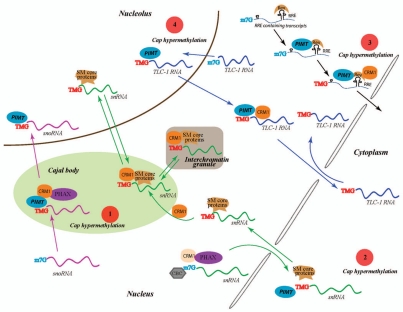
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of some of the CRM1 dependent nuclear and cytoplasmic events that influence the expression and function of hypermethylated cellular and viral RNAs. The hypermethylation of RNA caps is a complex process which occurs in different regions of the cells and appears to determine RNA trafficking inside the cell. Some proposed CRM1 dependent mechanisms that regulate post-transcriptional expression of TMG containing transcripts are indicated as follow. (1) m7G capped snoRNAs are targeted to “Cajal bodies” by CBC (cap binding complex) and PHAX (phosphorylated adapter for RNA export) where they are hypermethylated by PIMT and then bound by CRM1 through recognition of the TMG caps and transported to the nucleolus; (2) snRNAs are exported to the cytoplasm in a m7G-cap dependent manner. snRNAs bound by CBC, CRM1 and PHAX are exported to cytoplasm. The association of Sm core proteins with snRNA in cytoplasm recruits PIMT which hypermethylates the snRNA cap. The snRNA with TMG-cap are then re-imported into the nucleus in a complex with Sm core proteins. This snRNP interacts with CRM1 and localizes to Cajal bodies from where they travel to the nucleolus and interchromatin granules. (3) Rev binds to the cis-RRE motif in unspliced and partially spliced HIV-1 RNA and recruits PIMT which then hypermethylates the m7G-capped RNA. CRM1 binds to Rev and the TMG cap and transports the RNA into the cytoplasm. (4) Telomerase TLC-1 RNA (Telomerase component-1 RNA) also has been reported to acquire a TMG cap in the nucleus before being export through a CRM1 route into the cytoplasm.32