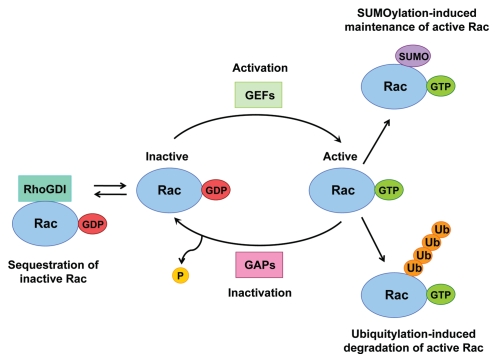
Figure 1.
Multiple mechanisms exist to regulate Rac activity. The Rac GTPase cycles between inactive GDP-bound and active GTP-bound states. Rac activation is facilitated by the action of GEFs, which promote GDP dissociation from Rac and allow GTP to bind instead. Through the association with GAPs the intrinsic GTPase activity of Rac is accelerated, thereby inactivating Rac. Through association with RhoGDIs Rac can be sequestered in its inactive state. Activated Rac can also be removed through Ubiquitylation-induced degradation, or it can be maintained following its modification by SUMO.