Figure 1.
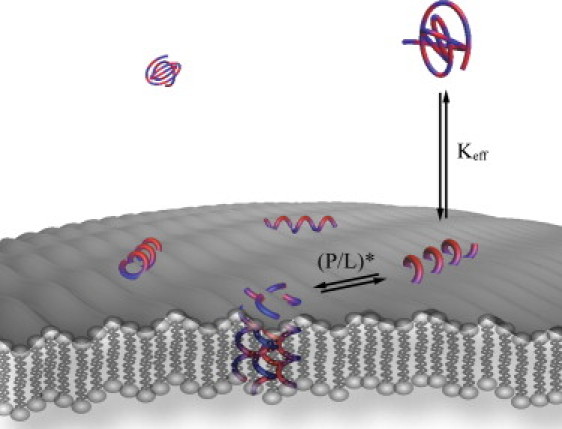
Illustration of an amphipathic peptide interacting with a lipid membrane. The peptide, which is shown in alternating blue and red to illustrate hydrophobic and hydrophilic amino acid residues, respectively, initially partitions onto the lipid membrane resulting in a conformational change of the peptide. Above the critical peptide/lipid ratio, (P/L)∗, the peptide inserts into the membrane and forms a pore. The insertion and pore formation are governed by the effective partition coefficient (Keff) and the pore-formation threshold (P/L)∗.
