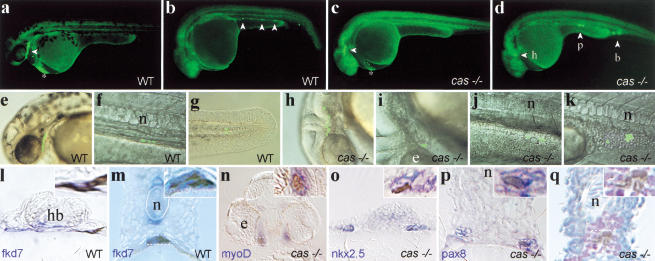
Figure 5.
Marginalmost blastomeres are transfated to mesoderm in cas embryos. One (b,d) or five (a,c) blastomeres of the most marginal row were labeled at 40% epiboly by uncaging the photoactivatable FD. At a later stage (30–36 h), embryos were photographed under low magnification epifluorescence (a–d, whole-mount side views, anterior to the left) or high magnification (e–k) to visualize cells harboring uncaged FD. Higher magnification views were superimposed on Nomarski pictures (e–k). (Open arrowheads) Fluorescent cells or groups of cells. (a,b,e–g) Fate acquired by marginalmost precursors in wild-type embryos. Progenitors contributed cells to the pharyngeal endoderm in the head (a,e) and the gut in the trunk (b,f), in addition to the hatching gland (a, *) and tail mesendoderm (g; see Bally-Cuif et al. 2000) as well as occasional mesoderm cells (blood in b). (c,d,h–k) Principal fates acquired by marginalmost precursors in cas embryos. Progenitors contributed mostly to head mesenchymal cells (c,h), myocardial cells (d,i), trunk pronephric duct cells (d,j), and blood (d,k) as well as hatching gland cells (c, *). (l–q) Then, embryos were fixed, stained with antifluorescein antibodies to reveal uncaged FD (brown/black) and by in situ hybridization with tissue specific markers (blue/purple) and analyzed by cross-section. A close-up view is provided in the upper right corner of each section and corresponds to the region included in the dotted rectangle. Wild-type cells are located in the pharyngeal endoderm (l) and the gut (m) and expressfkd7 (l,m). fkd7 is also expressed in the hypochord and the ventral brain. cas cells are located in mesoderm-derived tissues including head muscles (n), the heart primordia (o), the pronephric duct (p), and blood (q). These tissues are revealed by the markers indicated in the lower left corner, except for in q, in which blood is revealed by counterstaining with hematoxylin and eosin. (b) Blood; (e) eye; (h) heart; (hb) hindbrain; (n) notochord; (p) pronephros.