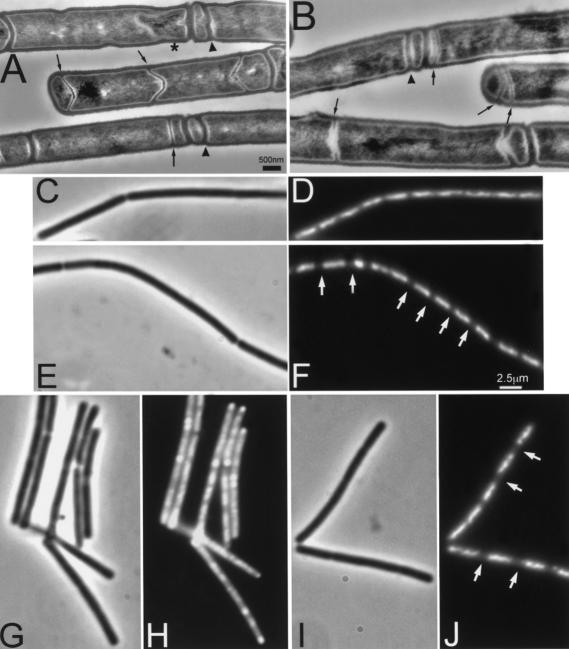
Figure 3.
Effect of minD and minD divIVA mutations on asymmetric septum formation and chromosome segregation during sporulation. Cultures of strains 1901 (minD; A,C,D,G,H) and 1920 (minD divIVA; B,E,F,I,J) were induced to sporulate by the resuspension method. (A,B) Samples were taken after 105 min for sectioning and transmission electron microscopy. Examples of minicell septa and thin (sporulation-type) septa are indicated by arrowheads and arrows, respectively. The star indicates a prespore being engulfed by the mother cell. (C–J) In a separate experiment, samples of sporulating cells were fixed at 90 (C–F) and 180 (G–J) min after initiation of sporulation. Samples were viewed by phase contrast (C,E,G,I) and fluorescence (DAPI) (D,F,H,J) microscopy. Arrowheads point to some condensed prespore nucleoids in the minD mutant cells, and arrows point to the larger gaps between nucleoids in the double mutant cells. Scale bar for A, 500 nm.