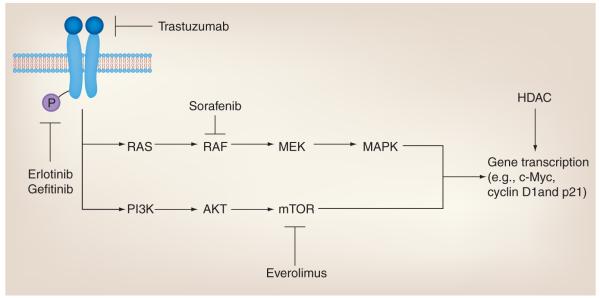
Figure 6. Role of acetylation in therapies targeting receptor tyrosine kinase signaling.
Mitogenic signaling involves ligand-induced dimerization and autophosphorylation of receptor tyrosine kinases (e.g., HER2/3 and EGF receptor), kinase signal transduction and target gene transcription, such as upregulation of c-Myc and cyclin D1, and downregulation of p21. Several therapies target these pathways, including trastuzumab, which inhibits HER2-ligand binding, erlotinib and gefitinib, which inhibit receptor tyrosine kinase autophosphorylation, and sorafenib and everolimus, which inhibit RAF and mTOR, respectively. HDACs also have been shown to mediate transcription of these cell cycle regulators. Therefore, combining HDAC inhibitors with receptor tyrosine kinase signaling inhibitors might further reduce tumor growth.
HDAC: Histone deacetylase.