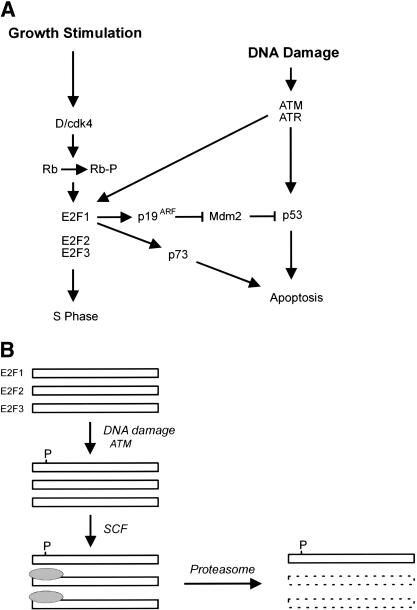
Figure 9.
Role of E2F1 in the DNA damage response. (A) A link between the Rb/E2F pathway and the DNA damage response. In addition to the role of ATM and ATR in inducing p53 accumulation, the results presented here identify E2F1 as a target for ATM and ATR in response to DNA damage. The consequence of the E2F1 induction could be seen as a further augmentation of p53 accumulation through an activation of p19ARF. In addition, given the ability of E2F1 to induce the p73 gene, the action through E2F1 could lead to a p53-independent effect on apoptosis. (B) Potential mechanism for ATM/ATR-mediated stabilization of E2F1. Previous work has documented the role of an SCF complex in targeting an amino-terminal domain of E2F1, leading to ubiquitin-dependent proteasome degradation. The site for ATM/ATR phosphorylation lies within this domain; as such, we speculate that the phosphorylation might prevent the interaction of the SCF complex with E2F1 and thus prevent degradation.