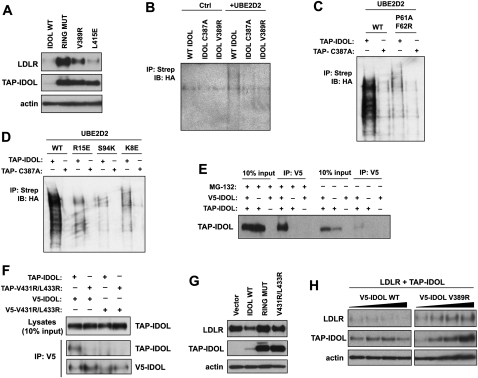
Figure 6.
Disruption of the IDOL–UBE2D interaction blocks LDLR degradation. (A) Mutations in the IDOL RING domain–UBE2D interaction interface inhibit LDLR degradation. Immunoblot analysis of protein levels in 293 cells transfected with LDLR and wild-type (WT) or mutant IDOL expression vectors. (B) UBE2D is unable to catalyze the autoubiquitination of mutant IDOL with a disrupted IDOL RING domain–UBE2D interaction. Immunoprecipitated TAP-IDOL, TAP-IDOL C387A, and TAP-IDOL V389R were incubated with UBE1, UBE2D2, and HA-ubiquitin. IDOL ubiquitination was detected by Western blot for HA-tagged ubiquitin associated with IDOL. (C) UBE2D2 mutated at the interface with IDOL is unable to catalyze IDOL autoubiquitination. Immunoprecipitated TAP-IDOL and TAP-IDOL C387A were incubated with UBE1, wild-type, or P61A/F62R UBE2D2 and HA-ubiquitin. IDOL ubiquitination was detected by Western blot for HA-tagged ubiquitin associated with IDOL. (D) Mutation of UBE2D2 residues predicted to be involved in IDOL specificity determination reduces the ability of UBE2D2 to support IDOL autoubiquitination. Immunoprecipitated TAP-IDOL and TAP-IDOL C387A were incubated with UBE1, wild-type, R15E, S94K, or K8E UBE2D2 and HA-ubiquitin. IDOL ubiquitination was detected by Western blot for HA-tagged ubiquitin associated with IDOL. (E) IDOL forms a dimer in vivo. 293 cells were transfected with vectors expressing TAP-IDOL and V5-IDOL. V5-IDOL in the cell lysate was immunoprecipitated with an anti-V5 antibody. The TAP-IDOL that coimmunoprecipitated with V5-IDOL was detected by immunoblotting using an anti-Flag antibody. (F) Structure-based mutations predicted to disrupt dimer formation prevent the coimmunoprecipitation of TAP-IDOL and V5-IDOL. 293 cells were transfected with the indicated combination of expression vectors. V5-IDOL and V5-mutant IDOL in the cell lysate were immunoprecipitated with an anti-V5 antibody. The coimmunoprecipitated TAP-IDOL was detected by immunoblotting using anti-Flag. (G) A dimer-defective IDOL mutant is unable to induce LDLR degradation. Immunoblot analysis of protein levels in 293 cells transfected with LDLR and wild-type or mutant IDOL expression vectors. (H) IDOL harboring a mutation in the IDOL RING domain–UBE2D interaction interface functions as a dominant negative in LDLR degradation assays. Immunoblot analysis of protein levels in 293 cells transfected with increasing amounts of V5-tagged wild-type or mutant IDOL, in addition to constant levels of LDLR and TAP-IDOL.