Figure 4.
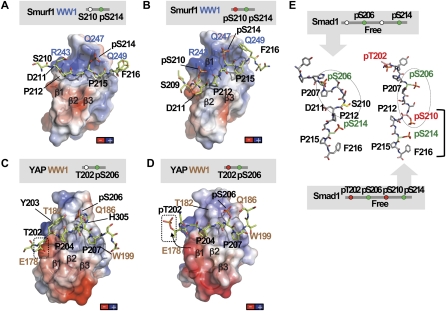
The GSK3 phosphorylated Smad1 linker prevents YAP binding. (A,B) Charge distribution on the surface of the Smurf1WW1 domain in complex with the Smad1 linker monophosphorylated at S214 (A) or diphosphorylated at S210 and S214 (B). Negatively charged patches are shown in red, and positively charged patches are shown in dark blue. Smurf1 WW1 is shown as a semitransparent surface, and Smad1 is shown as green sticks. Key residues in Smad1 (black) and Smurf1 WW1 (blue) are shown. The complex is shown in the same orientation as that of Figure 2. (C,D) Charge distribution on the surface of the YAP WW1 domain in complex with the Smad1 linker monophosphorylated at S206 (C) or diphosphorylated at T202 and S206 (D). The YAP WW1 domain is shown as a semitransparent surface and with the same orientation as in Figure 3. The position of T202 is shown in a box. The conformational change observed in pT202 is represented with an arrow. (E) Molecular simulations performed on two peptides corresponding to Smad1 phosphorylated at S206 and S214 (left) or at T202, S206, S210, and S214 (right). Key residues are labeled.