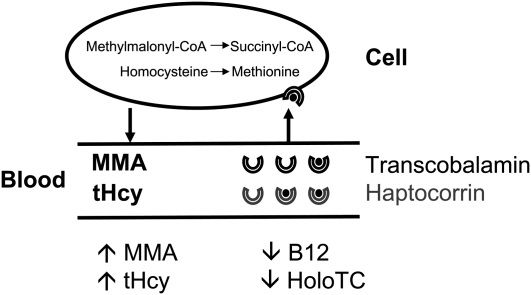
FIGURE 2.
Markers of cobalamin [vitamin B-12 (B12)] status. The figure shows the relation between vitamin B-12 deficiency markers. Holotranscobalamin (holoTC) transports vitamin B-12 into the cells by binding to a specific receptor, CD320. In the cell, vitamin B-12 acts as a coenzyme for 2 enzymes. Methionine synthetase (5-methyltetrahydropteroyl-l-glutamate:l-homocysteine-S-methyltransferase; EC 2.1.1.13), present in the cytoplasm, converts homocysteine (tHcy) to methionine. Methylmalonyl–coenzyme A (-CoA) mutases (methylmalonyl-CoA CoA-carbonylmutase; EC 5.4.99.2), which are present in the mitochondria, are involved in the conversion of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA. A decrease in holoTC results in a decrease in the cellular uptake of vitamin B-12. Once the cells become deficient, methylmalonic acid (MMA) and tHcy accumulate in the bloodstream; total vitamin B-12 concentration decreases.