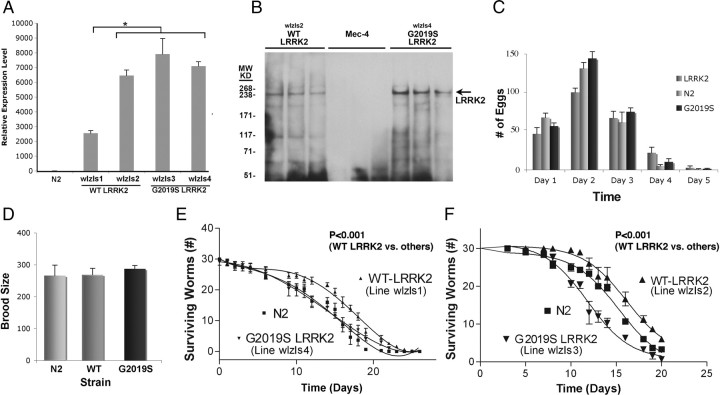
Figure 1.
Generation and characterization of C. elegans lines expressing WT or G2019S LRRK2. A, Quantification of LRRK2 mRNA expression for the WT LRRK2 lines (wlzIs1 and wlzIs2) and G2019S LRRK2 lines (wlzIs3 and wlzIs4). LRRK2 expression level was only significantly different for line wlzIs1 (*p < 0.001). B, Expression of LRRK2 in C. elegans lines. Three successive fractions eluted from the anti-V5 antibody column are shown for each nematode line. Lanes 1–3, WT LRRK2 (line wlzIs2); lanes 4–6, Mec-4::GFP (a line derived from the same lin-15 background as the LRRK2 lines); lanes 7–9, G2019S LRRK2 (line wlzIs4). The arrow points to the V5-LRRK2 at 250 kDa, which was eluted from the anti-V5 column. C, Number of eggs laid by N2 and transgenic lines. D, Analysis of total brood size for WT and G2019S LRRK2 (lines wlzIs2 and wlzIs4) demonstrates similar levels of fertility. E, F, Analysis of lifespan for WT and G2019S LRRK2 shows that C. elegans expressing WT LRRK2 (lines wlzIs1, wlzIs2) exhibit greater median lifespan compared with nontransgenic (N2) or G2019S LRRK2 lines (lines wlzIs3, wlzIs4). The lifespan data for E and F were generated with separate experiments.