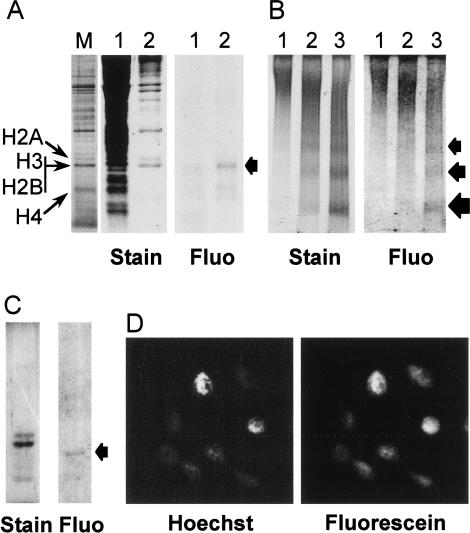
Figure 2.
Exogenous H2A/H2B dimers are internalized into Physarum cells, localized to the nuclei, and incorporated into chromatin. A solution of H2A/H2B* dimers (60 ng/μL) was deposited onto the upper cellular surface of Physarum fragments during S phase. (A) Exogenous H2A/H2B are localized in Physarum nuclei. The cellular localization of the exogenous proteins was analyzed by SDS-PAGE of cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions, shown in lanes 1 and 2, respectively. The gel was stained with Coomassie and the exogenous dimers were imaged by fluorography, as indicated. Physarum nuclear proteins were run as markers, with the histones as indicated (lane M). Fluo, Fluorograph. (B) Exogenous H2A/H2B dimers are incorporated into Physarum chromatin. Physarum nuclei were digested for 2, 5, and 10 min with MNase (lanes 1,2,3, respectively), and the products analyzed by nucleoprotein gel electrophoresis, followed by fluorography and ethidium staining, as indicated. (C) The presence of full-length exogenous proteins in mononucleosome and dinucleosome bands was confirmed by SDS-PAGE. (D) Fluorescently tagged exogenous H2A/H2B colocalizes with Hoechst-stained Physarum nuclei.