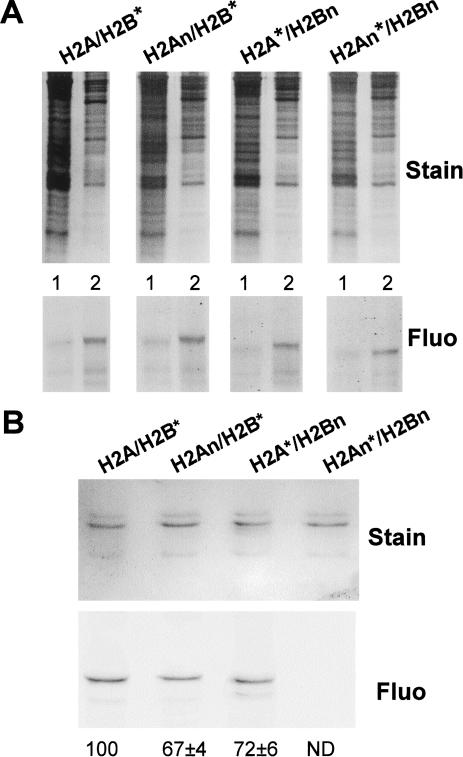
Figure 4.
Transport of histone H2A/H2B dimers into nuclei does not require the amino-terminal tails, but assembly into chromatin requires at least one tail domain. (Fluo) Fluorograph. (A) Cellular localization of exogenous histone H2A/H2B dimers. Cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions (lanes 1 and 2, respectively in each gel) were analyzed for each of the dimers shown at the top. The gels were stained and fluorographed, as indicated. (B) Assembly of exogenous H2A/H2B chromatin requires the amino-terminal-tail domains. Soluble chromatin was prepared from cells treated with each of the dimers listed at the top and analyzed as in Fig. 3C. The quantitation is the average of two independent experiments. ND, not determined.