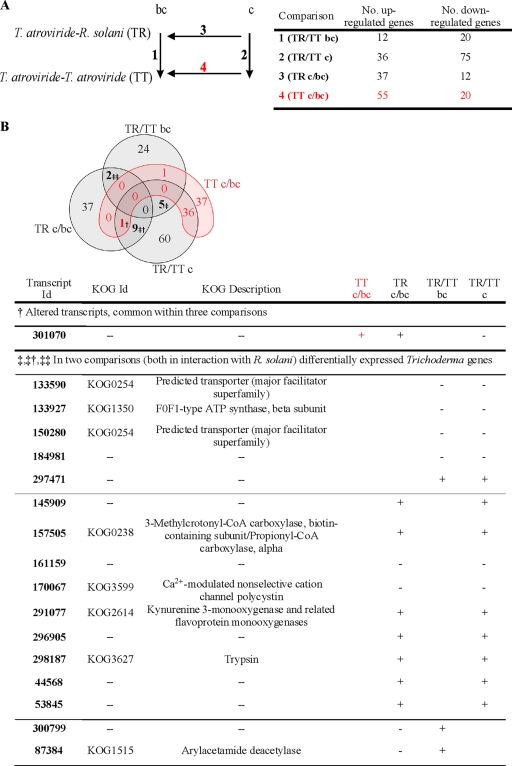
Fig. 1.
(A) Comparison of genome-wide transcription during confrontations against the host fungus R. solani with the control (T. atroviride against itself). 1 represents the number of differential genes (up- and downregulated) of 1 cm before direct contact (bc) with R. solani compared to the control (TR/TT bc), 2 gives the number of genes regulated during direct contact (c) with R. solani in relation with the corresponding control (TR/TT c), 3 compares gene expression levels of c and bc of T. atroviride with R. solani (TR c/bc), and 4 shows the relationship between genes expressed during c and 1 cm bc in the control (TT c/bc). (B) Four-set Venn diagram with the distribution of differentially expressed genes over the distinct comparisons. Whereas genes in common within TR/TT bc, TR/TT c, or TR c/bc are considered mycoparasitism relevant, genes common for TT c/bc are regarded as being less important during antagonism. The table displays the genes differentially regulated that are shared in three comparisons (†), prior to contact and during contact with R. solani (‡), during direct interactions with R. solani (‡†), and before visible contact with R. solani (‡‡). All these genes are given with their annotations according to the information available on the homepage of the T. atroviride genome project and their transcriptional regulation during different stages of interaction, with + being upregulated and − being downregulated. CoA, coenzyme A.