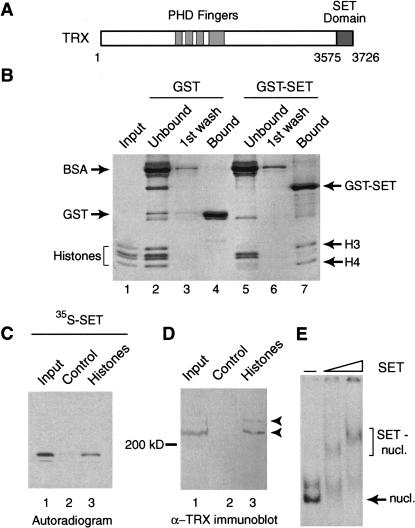
Figure 1.
The TRX SET domain binds histones and nucleosomes. (A) Schematic representation of the domain structure of TRX. Ignoring other conserved regions, only the PHD fingers, and the C-terminal SET domain are indicated. (B) The TRX SET domain interacts preferentially with the H3–H4 tetramer. GST and GST–SET domain fusion proteins were immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose and incubated with Drosophila core histones. Unbound proteins and first wash fractions were TCA precipitated. Protein complexes were resolved by 15% SDS-PAGE and visualized by Coomassie staining. Input corresponds to 30% of the material used in the binding reactions. (C) The TRX SET domain binds to a histone-affinity matrix. BSA–Sepharose control beads (lane 2) and histone–Sepharose beads (lane 3) were incubated with radiolabeled SET domain. Protein complexes were resolved by 15% SDS-PAGE and bound proteins were detected by autoradiography. Lane 1 represents 5% of the input. (D) TRX protein interacts with immobilized histones. BSA–Sepharose control beads (lane 2) and histone–Sepharose beads (lane 3) were incubated with Drosophila nuclear extracts. Bound proteins were resolved by 7.5% SDS-PAGE, transferred to nitrocellulose, and probed with an α-TRX antibody. Lane 1 represents 5% of the input. (E) The TRX SET domain binds mononucleosomes. In vitro assembled mononucleosomes were incubated with either no protein (lane 1) or with increasing concentrations of SET domain (lanes 2 and 3) and resolved by 4% native PAGE.