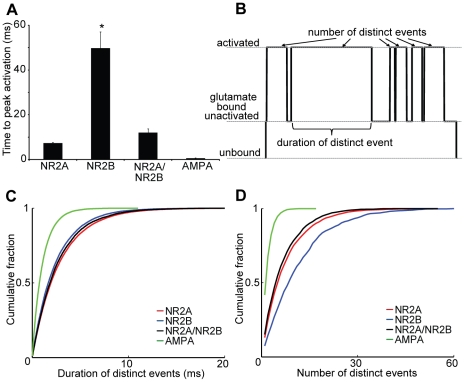
Figure 4. Slower kinetics and increased receptor flickering prolong NR2B activation.
The activation events for all NMDARs were analyzed to discern differences in the temporal activation patterns among subtypes. (A) NR2B-NMDARs reach peak activation significantly slower than NR2A-NMDARs and NR2A/NR2B-NMDARs (* p<0.05 NR2B vs NR2A and NR2B vs NR2A/NR2B). (B) Receptor “flickering”, defined by the ability for a receptor to have multiple activation events without glutamate unbinding was analyzed using cumulative distributions to (C) demonstrate that NR2A-NMDARs (red) have significantly longer durations of individual events compared to NR2B-NMDARs (blue), triheteromeric NMDARs (black) and AMPARs (green) (KS test - p<0.01). (D) However, NR2B-NMDARs have significantly more distinct events per binding compared to other subtypes (KS test - p<0.01).