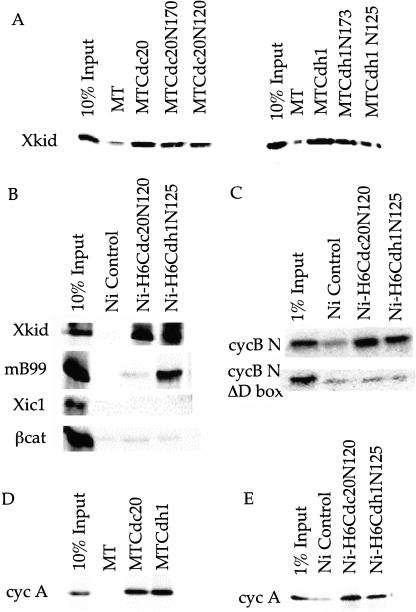
Figure 2.
N-terminal activator binds substrate with specificity. (A) Binding assays as above, using myc-tagged deletion mutants of Cdh1 and Cdc20. Myc-tagged fragments containing the N-terminal 120 amino acids of Cdc20 and the N-terminal 125 amino acids of Cdh1 were sufficient for binding of Xkid. (B) Bacterially expressed his-tagged N-terminal hCdc20 bound to nickel beads (Ni-H6Cdc20N120) binds Xkid, but not mB99. Bacterially expressed his-tagged N-terminal hCdh1 bound to nickel beads (Ni-H6Cdh1N125) binds both Xkid and mB99. Neither Ni-H6Cdc20N120 nor Ni-H6Cdh1N125 binds β-cat or Xic1. (C) Both N-terminal bacterially expressed hCdc20 and hCdh1 bind the N-terminal fragment of Xenopus cyclin B containing the D box, but fail to recover the D-box deleted N-terminal cyclin B. (D) In vitro-translated cyc A binds MTCdc20 and MTCdh1, but not to MT alone. Ten percent of input is shown in the left-most lane. (E) Bacterially expressed his-tagged N-terminal hCdc20 or N-terminal hCdh1 bind ∼1–5% of in vitro translated cyc A.