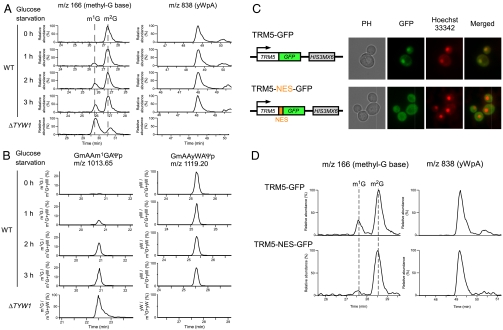
Fig. 2.
Glucose starvation induces the accumulation of m1G37-bearing tRNAPhe in the nucleus. (A) LC/MS analyses of the total nucleosides in the tRNAPhe molecules isolated from yeast cells (BY4742) after 0h (uppermost panels), 1h (second panels), 2h (third panels), and 3h (fourth panels) of glucose starvation. As a control, the nucleosides of the tRNAPhe molecules that were isolated from ΔTYW1 are shown in the lowermost panels. The Left panels show the mass chromatograms of the base-related ion (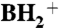 ) of monomethylated guanosine (m/z 166), which detect m1G and m2G. The Right panels show the mass chromatogram of the proton adduct of yWpA (m/z 838). (B) LC/MS RNA fragment analyses of the RNaseA-digested tRNAPhe molecules. The panels show the mass chromatograms that detect the doubly charged ions of the anticodon-containing fragments that bear m1G (Left panels, m/z 1,013.65) and yW (Right panels, m/z 1,119.20). The vertical axes display the apparent ratio of m1G or yW, which is calculated on the basis of the intensity of the m1G- and yW-containing fragments. (C) The TRM5-GFP (Upper) and TRM5-NES-GFP (Lower) constructs are shown. The photos show the phase contrast (PH), GFP-fluorescence, Hoechst 33342, and merged images for each strain. (D) LC/MS analyses of the total nucleosides in the tRNAPhe molecules that were isolated from the TRM5-GFP (Upper) and TRM5-NES-GFP (Lower) strains after 4h of glucose starvation. The Left and Right panels show the mass chromatograms of the base-related ion (
) of monomethylated guanosine (m/z 166), which detect m1G and m2G. The Right panels show the mass chromatogram of the proton adduct of yWpA (m/z 838). (B) LC/MS RNA fragment analyses of the RNaseA-digested tRNAPhe molecules. The panels show the mass chromatograms that detect the doubly charged ions of the anticodon-containing fragments that bear m1G (Left panels, m/z 1,013.65) and yW (Right panels, m/z 1,119.20). The vertical axes display the apparent ratio of m1G or yW, which is calculated on the basis of the intensity of the m1G- and yW-containing fragments. (C) The TRM5-GFP (Upper) and TRM5-NES-GFP (Lower) constructs are shown. The photos show the phase contrast (PH), GFP-fluorescence, Hoechst 33342, and merged images for each strain. (D) LC/MS analyses of the total nucleosides in the tRNAPhe molecules that were isolated from the TRM5-GFP (Upper) and TRM5-NES-GFP (Lower) strains after 4h of glucose starvation. The Left and Right panels show the mass chromatograms of the base-related ion (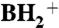 ) of monomethylated guanosine (m/z 166) and the proton adducts of yWpA (m/z 838), respectively.
) of monomethylated guanosine (m/z 166) and the proton adducts of yWpA (m/z 838), respectively.