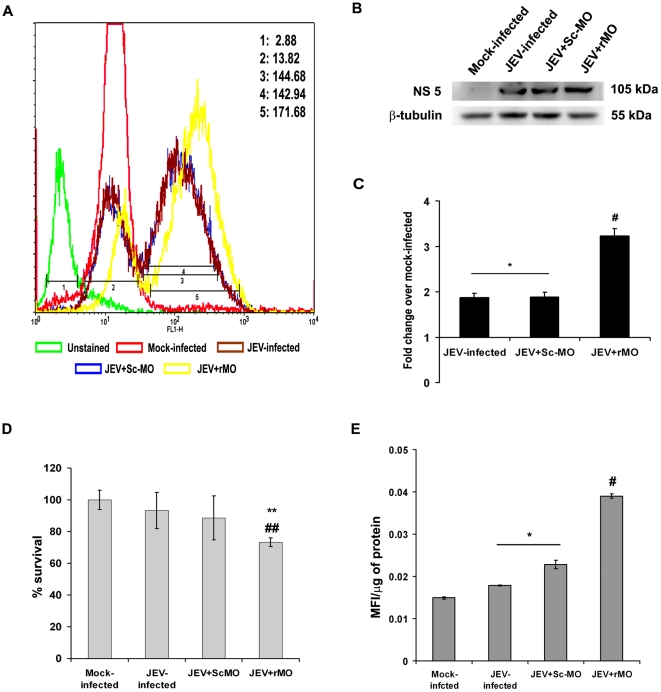
Figure 8. Increased oxidative stress, viral load and decreased survivability of N2a following RIG-I ablation.
Flow cytometric analysis carried out from cells of all treatment groups to detect intracellular JEV antigen showed significant increase post RIG-I ablation when compared to only JEV-infected or JEV+ScMO groups. The mean fluorescence intensities obtained from each group are depicted in the figure. (1-Unstained, 2-Mock-infected; 3-JEV-infected, 4-JEV+Sc-MO, 5-JEV+rMO) (A). Immunoblot analysis to detect JEV NS-5 expression also showed enhancement in JEV+rMO when compared to either JEV-infected or JEV+ScMO groups (B&C). (*p<0.05, when compared to mock–infected, #p<0.05 when compared to JEV-infected group). No statistically significant change in the viability of N2a post 24 h of JEV-infection was observed. However, RIG-I ablation resulted in significantly decreased viability compared to mock-infected as well as JEV-infected groups (D). (**p<0.05 when compared to mock-infected; ##p<0.05 when compared to JEV-infected). ROS production, a hallmark of JEV infection, showed significant increases in JEV-infected and JEV+Sc-MO groups when compared to mock-infected groups which on RIG-I ablation showed further increase even when compared to JEV-infected group (E). (*p<0.05 when compared to mock-infected; #p<0.05 when compared to JEV-infected). Data is representative of 3 independent experiments.