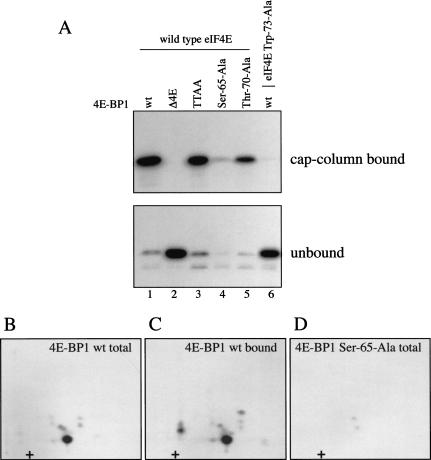
Figure 6.
Phosphorylation of Ser 65 alone is insufficient to effect release from eIF4E. Bacterially expressed wild-type and mutant GST–4E-BP1 proteins were phosphorylated for 15 min with recombinant ERK2 in the presence of [γ-32P]ATP. Labeled 4E-BP1 proteins were incubated for 1 h with equimolar concentrations of recombinant GST–eIF4E proteins. (A) Complexes were recovered on an m7GDP-sepharose column (cap-column bound), and analyzed by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. Fractions not retained on the cap column (unbound) were analyzed similarly. Δ4E is a 4E-BP1 mutant deleted in the binding site for eIF4E, and TTAA is the double point mutant Thr 37-Ala/Thr 46-Ala. Trp 73-Ala is an eIF4E mutant unable to bind to 4E-BP1. (B–D) Phosphopeptide mapping of ERK2-phosphorylated 4E-BP1. (B) Phosphopeptide map of 4E-BP1 phosphorylated in vitro by ERK2. (C) Phosphopeptide map of 4E-BP1 phosphorylated in vitro by ERK2, and recovered on a cap column. (D) Phosphopeptide map of the Ser 65-Ala mutant phosphorylated in vitro.