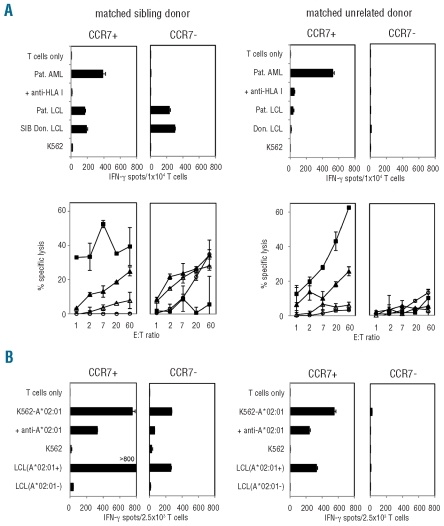
Figure 3.
Parallel analysis of CD8 T-cell subsets for reactivity to HLA-matched AML blasts and to K562-HLA mismatch cells. MLLC and MLR were initiated with sorted CCR7pos and CCR7neg CD8 T-cell subsets from healthy individuals. Stimulator cells were primary AML blasts with complete HLA class I-match (4 digits) in MLLC and K562-HLA mismatch cells in MLR. (A) Representative functional data from MLLC of a sibling donor/patient pair SIB 369/MZ369-AML (left panels) and an unrelated donor/patient pair Don 069/MZ653-AML (right panels) are shown. Cultures were analyzed on d19 (i.e. 5 days after second AML restimulation on d14) in IFN-γ ELISpot (upper panel) and 51Cr-cytotoxicity assays (lower panel). Targets of 51Cr-assays were AML blasts (■), patient-derived LCL (▴), donor-derived LCL (▵), and K562 cells (○). (B) Results from MLR of donors SIB 369 and Don 069, in which HLA-A*02:01 was used as the mismatch allele (for HLA types see Online Supplementary Table S1) are shown. Cultures were screened on d19 for allo-HLA-A*02:01-reactive CD8 T cells in IFN-γ ELISpot assays. LCL from HLA-A*02:01-positive and -negative third-party donors were included as control targets.