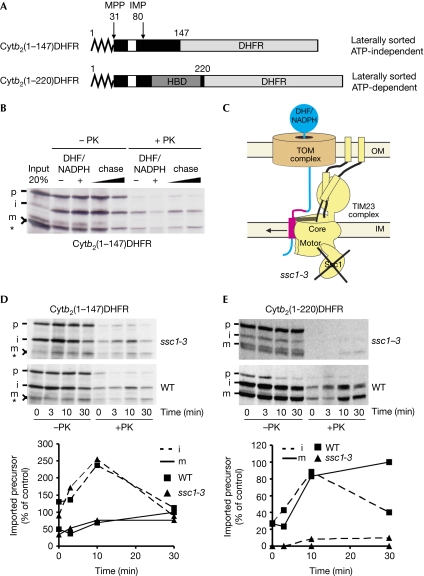
Figure 1.
Translocation arrest of substrates laterally sorted by the TIM23 complex. (A) Schematic representation of fusion proteins consisting of different segments of yeast cytochrome b2 (Cytb2; black box) and mouse DHFR (grey box). Zigzag line denotes the presequence and white boxes denote the transmembrane segment of b2. (B) 35S-labelled cytb2(1–147)DHFR was imported into wild-type mitochondria in the presence or absence of DHF and NADPH. DHF/NADPH-treated samples were reisolated, washed and incubated further for 5 and 20 min (chase). Samples were treated with PK where indicated and analysed by SDS–PAGE and autoradiography. Asterisk indicates a translation product arising from an internal methionine. (C) Schematic representation of the translocation arrest and lateral release in the ssc1-3 mutant mitochondria, which carry a temperature-sensitive mutant of mitochondrial Hsp70. (D,E) Wild-type and ssc1-3 mitochondria were preincubated for 10 min at 37 °C and used for import of indicated precursor proteins in the presence of DHF and NADPH. Mitochondria were reisolated, incubated further without NADPH/DHF for the indicated time periods and subsequently treated as described in (B). Autoradiographs are shown in the upper panels and quantifications of PK-protected material in the lower panels. PK-protected mature form at 30 min in WT was set to 100%. DHFR, dihydrofolate reductase; HBD, haem-binding domain; i, intermediate form of imported protein; IM, inner membrane; IMP, inner membrane protease; m, mature form of imported protein; MPP, mitochondrial processing peptidase; NADPH, nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (reduced form); OM, outer membrane; p, precursor form of imported protein; PK, proteinase K; SDS–PAGE, SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis; WT, wild-type.