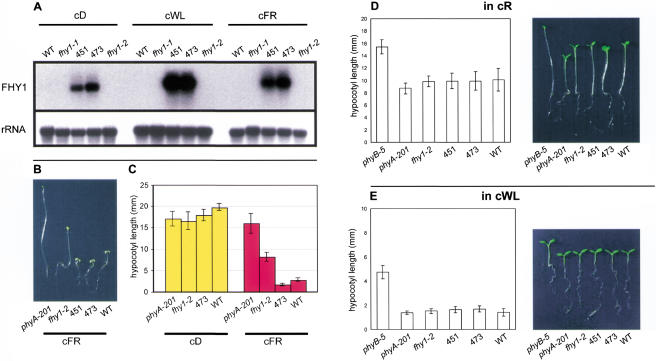
Figure 4.
Seedlings overexpressing FHY1 exhibit enhanced cFR responses. (A) Plants containing the 35S::FHY1 construct have elevated levels of FHY1 transcript. (Upper panel) FHY1 transcripts are detectable in 451 and 473 (fhy1-2 lines containing a 35S::FHY1 transgene) but not detectable in wild type (WT), fhy1-1, or fhy1-2 in cD, cWL, or cFR. This was a shorter exposure than in Figure 3A, thus explaining why FHY1 transcripts are visible in cD-grown WT in Figure 3A but not in this figure. (Lower panel) rRNA loading control for hybridization in upper panel. (B) 35S::FHY1;fhy1-2 hypocotyls exhibit enhanced responses to cFR. Seedlings from lines 451 and 473 (35S::FHY1;fhy1-2) have shorter hypocotyls in cFR than WT, fhy1-2, or phyA-201. (C) Histogram shows mean and standard error of hypocotyl lengths of seedlings grown in cD and cFR (n = 25–38). Seedlings grown in cD are indistinguishable from one another. 473 (35S:FHY1;fhy1-2) hypocotyls are significantly shorter than WT hypocotyls in cFR. (D) 35S::FHY1;fhy1-2 hypocotyls do not exhibit enhanced responses to cR. Photograph and histogram of seedlings of various genotypes. Histogram shows mean and standard error of hypocotyl lengths (n = 24–28). For reference, the phyB-5 mutant, which exhibits a long hypocotyl in cR, is shown. The 451 and 473 lines are indistinguishable from WT. (E) 35S::FHY1;fhy1-2 hypocotyls do not exhibit enhanced responses to cWL. Photograph and histogram of seedlings of various genotypes. Histogram shows mean and standard error of hypocotyl lengths (n = 18–23). The 451 and 473 lines are indistinguishable from WT.