Fig. 3. Sequential events during JCV life cycle.
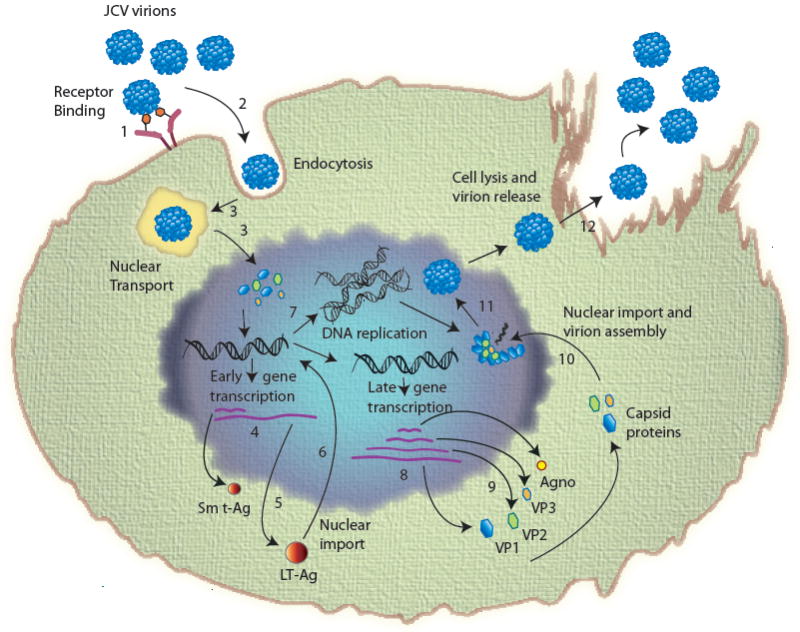
(1) Adsorption of virus to the cell surface receptors; (2) entry by clathrin-mediated endocytosis; (3) uncoating of virions and nuclear transport (uncoating takes place either in the either in endoplasmic reticulum or in the nucleus); (4) transcription of early coding region; (5) translation to produce early regulatory proteins, LT-Ag, Sm t-Ag and T’ proteins (T’135, T’136 and T’165); (6) import of LT-Ag into nucleus to initiate viral DNA replication and late gene activation; (7) replication of viral genome; (8) transcription of viral late genome; (9) translation of viral late transcript to produce agnoprotein and capsids (VP1, VP2 and VP3); (10) Nuclear import of capsid proteins; (11) assembly of viral progeny in the nucleus; (12) release of virions from infected cells.
Agno: Agnoprotein; JCV: JC virus; LT-Ag: Large T antigen; Sm t-Ag: Small t antigen
