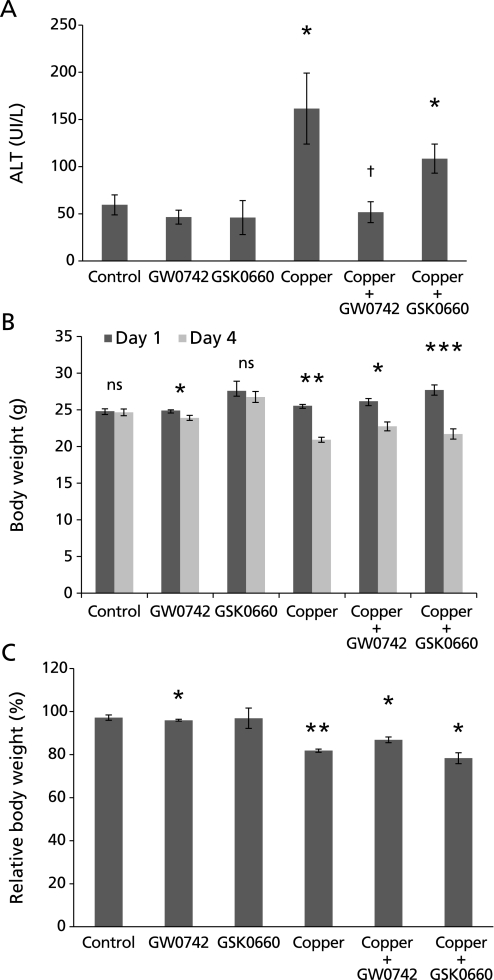
Fig. 2.
Serum ALT and mice body weight. (A) Control mice had an average ALT concentration of 59.5 UI/L, concentration that significantly increased to 161 UI/L in mice treated with copper. Serum ALT in mice treated with copper and GSK0660 was 108 UI/L, which is not significantly different to the increase observed in mice treated with copper alone. ALT in mice treated with copper and GW0742 was 46.5 UI/L, what is significantly lower than in mice treated with copper alone and comparable to control group (*p<0.05 vs control; †p<0.05 vs copper). (B, C) Body weight was assessed before treatment on day 1 and before sacrifice on day 4. Average body weight and relative changes in body weight between day 1 (100%) and day 4 can be observed in B and C respectively. Copper alone induced a significant 18% decrease in body weight, decrease that was still significant but less important in those that also received GW0742 (13%). Mice treated with copper and GSK0660 lost a significant 20% of body weight. GW0742 induced a small but significant 3% body weight loss. Error bars represent SEM and p value was assessed by Mann-Whitney-Wilcoxon U Test (*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001).