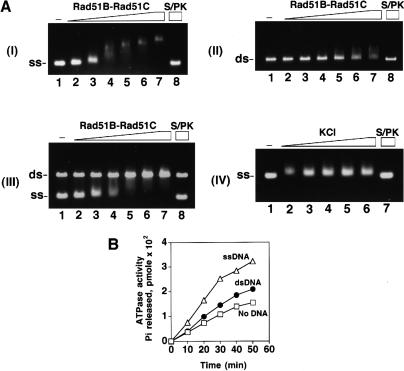
Figure 3.
Rad51B–Rad51C binds DNA and hydrolyzes ATP. (A) Rad51B–Rad51C complex (0.15, 0.3, 0.45, 0.6, 0.75, and 0.9 μM in lanes 2–7, respectively) was incubated with φX ssDNA (12 μM nucleotides in panel I; designated as ss), φX dsDNA (4 μM base pair in panel II; designated as ds), or with both the ssDNA and dsDNA (panel III) for 10 min at 37°C and then run in a 0.9% agarose gel. The DNA species were stained with ethidium bromide. In lane 8 of all three panels, the nucleoprotein complex formed with 0.9 μM of Rad51B–Rad51C complex was treated with 0.5% SDS and 500 μg/mL proteinase K at 37°C for 5 min before loading onto the agarose gel. In lane 1 of all three panels, DNA was incubated in buffer without protein. In panel IV, Rad51B–Rad51C complex (0.3 μM) was incubated with ssDNA (12 μM nucleotides) in the presence of increasing concentrations (50, 100, 150, 200, and 250 mM in lanes 2–6, respectively) of KCl at 37°C for 10 min and then analyzed. (B) Rad51B–Rad51C, 1.8 μM, was incubated with 1 mM ATP in the absence of DNA (designated by the squares) and in the presence of ssDNA (20 μM nucleotides; designated by the triangles) or dsDNA (20 μM base pairs; designated by the closed circles) for the indicated times at 37°C.