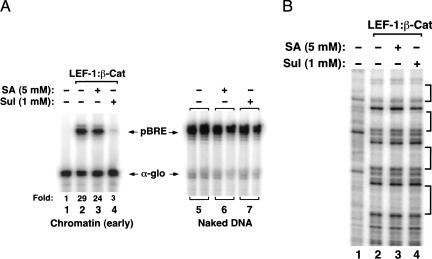
Figure 6.
LEF-1–β-cat transactivation on chromatin in vitro is inhibited by the NSAID, sulindac. (A) (Left panel) Analysis of the effects of NSAID on LEF-1–β-cat transcription of pBRE chromatin templates in vitro. Chromatin was assembled in the absence of enhancer factors (lane 1) or in the presence of 120 nM ΔAD-LEF and 120 nM β-cat (lanes 2–4), in the presence of 5 mM salicylic acid (lane 3) or 1 mM sulindac (lane 4). (Right panel) Analysis of the effects of NSAIDs on nonchromatin pBRE DNA templates. Reactions either lacked NSAIDs (lane 5) or contained either 5 mM salicylic acid (lane 6) or 1 mM sulindac (lane 7). Arrows indicate pBRE (chromatin) and α-globin (nonchromatin) transcripts. (B) DNase I footprint analysis of the effects of NSAIDs on binding of the LEF-1–β-cat complex to chromatin. Chromatin was assembled in the absence of enhancer factors (lane 1) or in the presence of 120 nM each of ΔAD-LEF and β-cat (lanes 2–4), incubated with either 5 mM salicylic acid (lane 3) or 1 mM sulindac (lane 4). Brackets indicate the four LEF/TCF binding sites in the pBRE enhancer.