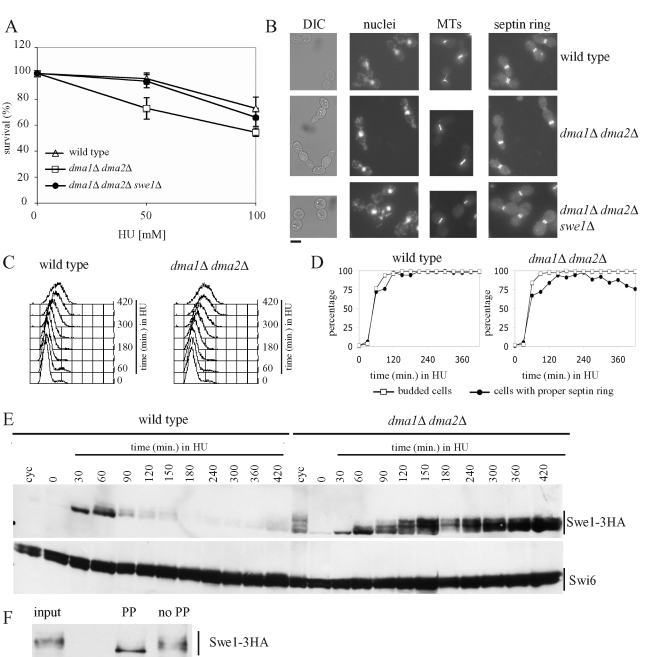
FIGURE 3:
Effect of the lack of Dma proteins on cell viability, cell morphology, and Swe1 stability in HU-treated cells. (A) Serial dilutions of stationary-phase cultures of the indicated strains were spotted on YEPD plates containing the indicated HU concentrations and incubated for 4 d at 25°C. Colony-forming units were then counted to determine cell viability. Plotted values are the mean values ± SD (bars) from three independent experiments. (B) Exponentially growing cultures of wild-type (W303), dma1Δ dma2Δ (ySP1569), and dma1Δ dma2Δ swe1Δ (ySP3164) cells were transferred to YEPD medium containing 200 mM HU at 25°C. After 7 h, cell samples were taken for cell morphology analysis (DIC) and for in situ immunofluorescence analysis of nuclei, mitotic spindles (MTs), and septin ring deposition by using DAPI staining, anti-tubulin antibodies and anti-Cdc11 antibodies, respectively. Bar, 5 μm. (C–E) Exponentially growing (cyc) cultures of SWE1-3HA (ySP3427) and dma1Δ dma2Δ SWE1-3HA (yRF661) cells were arrested in G1 by α-factor and released from G1 arrest at 25°C in YEPD medium containing 200 mM HU (time 0). At the indicated times, cell samples were taken for FACS analysis of DNA contents (C), for scoring budding and septin ring formation (D), and for determining Swe1 levels by Western blot analysis with anti-HA and anti-Swi6 (loading control) antibodies (E). (F) Protein extracts of dma1Δ dma2Δ SWE1-3HA cells grown for 3 h in HU-containing medium (input) were immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibodies and the immunoprecipitate was incubated for 30 min at 30°C with 20 units/μl lambda phosphatase (PP) or with reaction buffer only (no PP).