Figure 4.
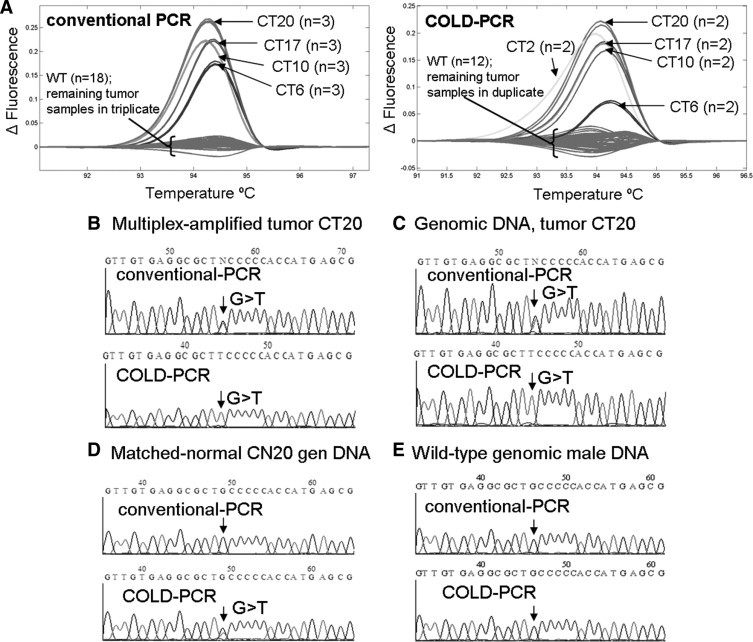
In the exon 5 (148bp) amplicon, several mid- to high- abundance mutations were detected in the tumor samples, including colorectal tumor sample CT20. Additionally, after analyzing COLD-PCR amplicons with HRM (A), a low-abundance mutation was detected in CT2; however, this mutation was not detectable in conventional PCR amplicons. A mid- to high-abundance mutation was detected in CT20 by HRM for both PCR amplicons of the exon 5 148bp amplicon (in addition to the previously discussed low-abundance mutations in exons 8 and 9). Sanger sequencing analysis (sense strand) of the multiplexed-PCR product (B) and genomic DNA (C) for CT20 revealed a heterozygous G>T mutation in conventional PCR amplicons; the T allele was enriched during COLD-PCR. The mutation was also detected in the COLD-PCR amplification of the matched normal tissue (D), suggesting that the putatively normal sample may contain tissue from the tumor margin. This G>T is unlikely to be artifact of COLD-PCR as it is not observed in the wild-type (genomic human male) amplicons (E).
