Figure 1.
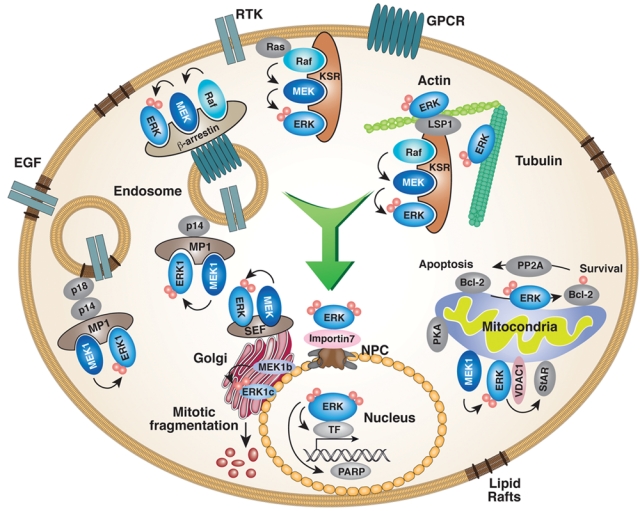
ERK1/2 distribution within the various compartments of the cell. The activation of the ERK1/2 cascade results in a significant translocation of the ERK1/2 molecules to the nucleus, which is mediated by interaction with importin7 to induce mainly proliferation and differentiation. In addition, ERK1/2 translocate into various cellular organelles usually because of interaction with specific scaffold proteins. In each of these organelles, ERK1/2 can either regulate intrinsic activities or direct ERK1/2 signals to nearby cytoplasmic substrates (for details, see text).
