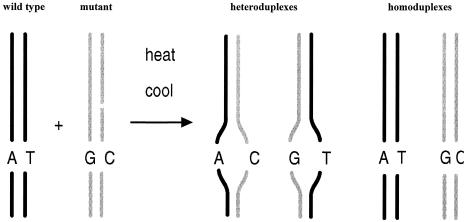
Fig 1.
Schematic of heteroduplex formation for mutation analysis. The PCR products of wild-type and mutant allele, differing by as little as a single base pair, are denatured by heating and reannealed by slow cooling. The resultant wild-type and mutant homoduplexes melt at higher temperatures than the mismatch containing wild-type/mutant heteroduplexes. The difference in melting temperature between homo- and heteroduplexes is the basis for the identification of mutations by DNA chromatography