Fig. 3.
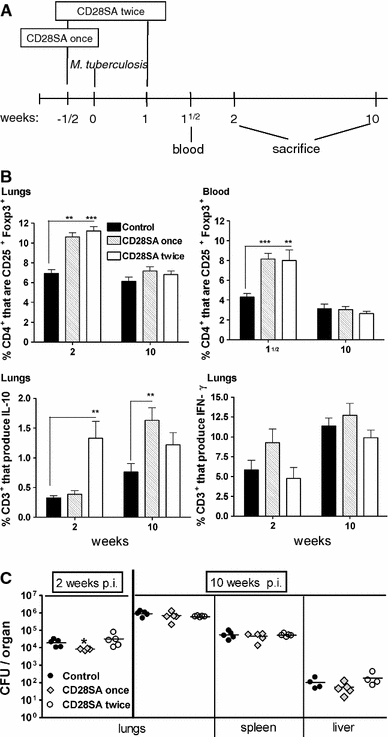
CD28SA treatment during M. tuberculosis infection increases the percentage of CD25+Foxp3+ T-cells but has no major effect on bacterial burden. a BALB/c mice were treated i.p. with CD28 superagonist (CD28SA, D665, 50 μg/mouse) or isotype control (MOCP31) either ½ week prior (CD28SA once) or ½ week prior and 1 week (CD28SA twice) post aerosol with 100 CFU/lung of M. tuberculosis. Mice were bled at 1½ week and killed at 2 and 10 weeks post-infection. b Expression of CD25+ and Foxp3+ on CD4+-gated cells was measured by flow cytometry in collagenase-treated lung and in peripheral blood lymphocytes. The percentage of CD3+ lung cells producing IL-10 and IFN-γ are also represented. Lung cells were harvested following collagenase treatment and stimulated with PMA and ionomycin in the presence of monensin for 4 h and subjected to intracellular staining. c The bacterial load in lungs, spleen, and liver were determined at 2 and 10 weeks post M. tuberculosis infection. Data are presented as log10 CFU per organ. Individual bacterial titers are given together with group medians. Statistical analysis was performed using an unpaired two-tailed Student’s t-test. Data are represented as means ± SEM (n = 5 mice/group; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). All data are obtained from one experiment
