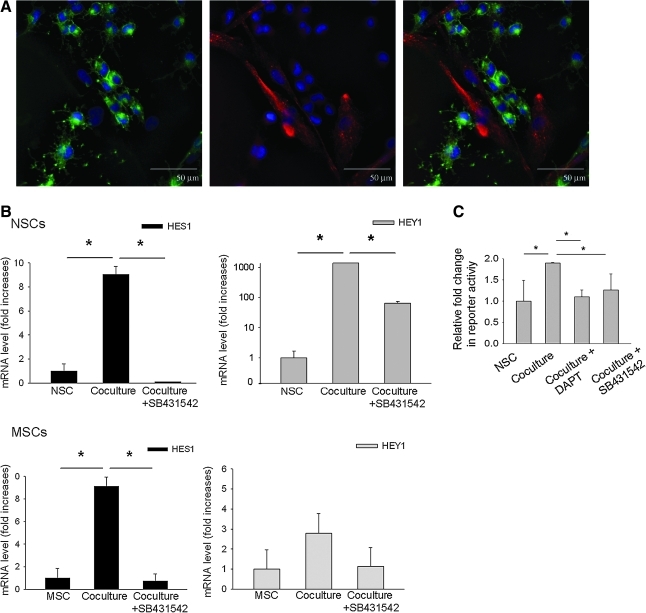
FIG. 5.
Notch signaling was increased in the cocultures and decreased by an inhibitor of TGFβ signaling. (A) rNSCs in coculture expressed Notch 1 (green). Also, hMSCs contacting rNSCs expressed the Notch ligand Jagged 1 (red). Nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue). Scale bar = 50 μm. (B) Real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction assays for the Notch downstream targets HES1 and HEY1. In coculture, expression of both HES1 and HEY1 was increased in rNSCs and that of HES1 was increased in hMSCs. An inhibitor of TGFβ signaling (SB431542) decreased expression of HES1 and HEY1 in the rNSCs and HES1 in the hMSCs (t-test: *P < 0.01 vs. coculture). (C) Notch intracellular signaling in the rNSCs was assayed using an inducible reporter construct for the recombination signal binding protein for immunoglobulin kappa J region (RBP-Jk) protein, a downstream modulator of Notch signaling. Coculture significantly increased intracellular Notch signaling. Both the TGF(inhibitor (SB431542) and the γ-secretase inhibitor (DAPT) decreased Notch signaling [1-way ANOVA, F(3,8) = 8.41, *P < 0.05 vs. coculture].