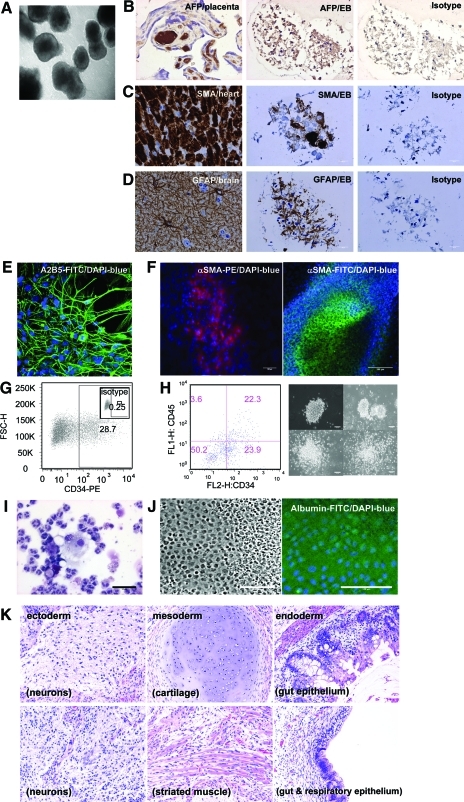
FIG. 5.
Pluripotency of MnOFiPS cells (clone 6). (A–D) In vitro differentiation of MnOFiPS cells by embryoid body (EB) formation. (A) EB formation of MnOFiPS cells at day 15. Multiple EBs consisted of cells representing 3 embryonic germ layers indicated by immunohistochemistry staining: (B) endoderm marker αFP, (C) mesoderm marker SMA, and (D) ectoderm marker GFAP. Human fetal placenta, monkey heart tissue, and monkey brain tissue were used as positive controls respectively. Scale bars, 20 μm. (E–H) Direct differentiation of MnOFiPS cells in vitro. (E) MnOFiPS cells differentiated into neuronal precursors (A2B5+) by co-culturing with PA6 murine stromal cells after 14 days. (F) MnOFiPS cells differentiated into SMA+ cardiomyocytes 15 days after actinA activation. Scale bars, 100 μm. (G) Hematopoietic differentiation of MnOFiPS cells by co-culturing with OP9 stromal cells generated CD34+ cells on day 11. (H) Hematopoietic differentiation of MnOFiPS cells by EB formation supplemented with cytokines generated CD34+ CD45+ cells, which formed colonies after 14 days. Scale bars, 100 μm. (I) Colonies contain neutrophils, macrophages, and eosinophils shown by Giemsa staining. Scale bars, 50 μm. (J) MnOFiPS cells differentiated into albumin+ hepatocytes. Scale bars, 100 μm. (K) MnOFiPS cells are pluripotent in vivo. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of teratoma tissue derived from MnOFiPS cells. Cells were transplanted into testis of NOD/SCID mice, and the teratomas were harvested 6 weeks after injection. GFAP, glial fibrillary acidic protein; SMA, smooth muscle actin. Color images available online at www.liebertonline.com/scd