Fig. 1.
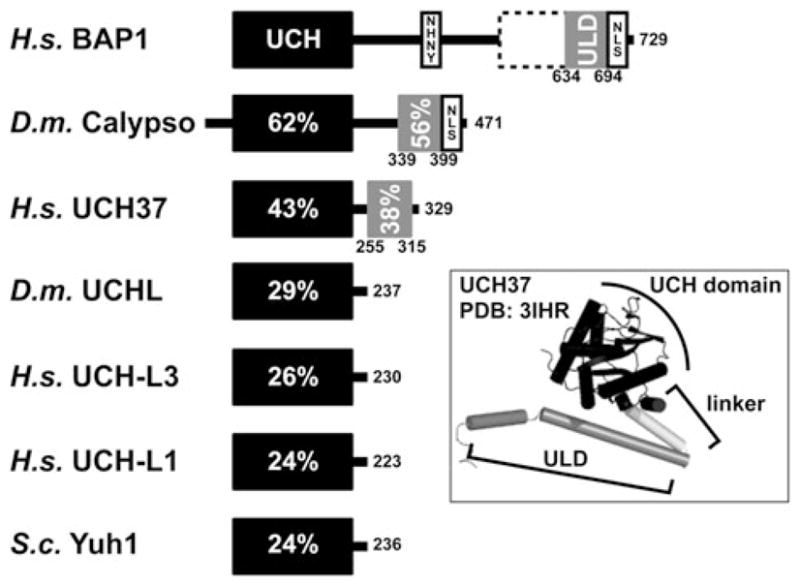
Domain architecture and sequence conservation of human, fruit fly, and yeast UCH DUBs. Human BAP1 is composed of an N-terminal UCH domain (res. 1–250), an HBM (NHNY, res. 363–366), a region that mediates association with BRCA1 (res. 596–721), a 60 residue helical motif that shares conservation with UCH37 (ULD for UCH37-like domain, res. 634–694), and a bona fide nuclear localization signal (NLS, RRRKGR, res. 717–722). The UCH domains of other human, yeast, and fruit fly DUBs are depicted by black bars and percentages reflect the sequence identity compared to BAP1. Calypso and UCH37 also contain ULDs (gray bars) and Calypso contains a putative NLS at its C-terminus (RRRKGR, res. 459–464). The inset maps the UCH and ULD domains of UCH37 onto its crystal structure. The UCH domain, shown in black, is connected to the helical ULD, shown in gray, by a short helical linker
