Fig 2.
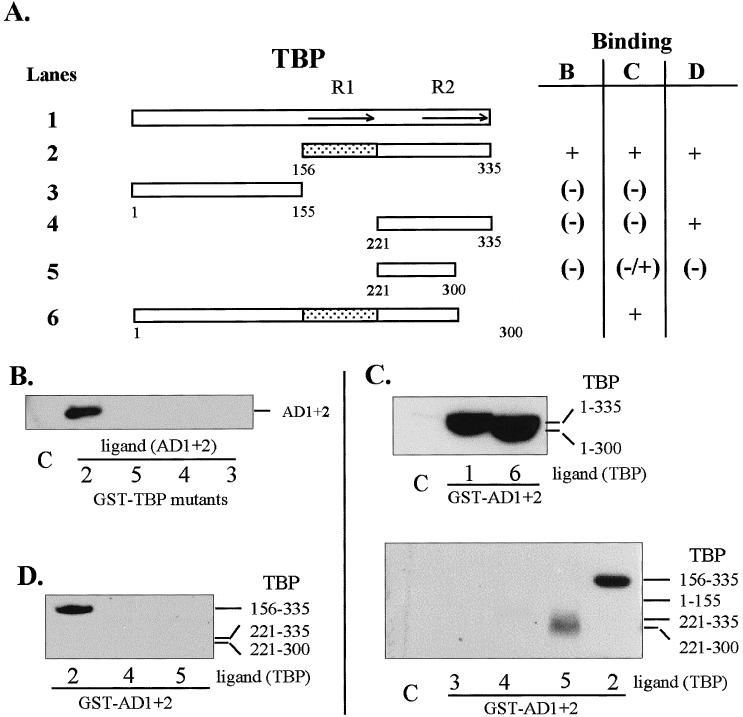
Regions of TBP that interact in vitro with HSF1 AD1+2. (A) Diagrammatic summary of interactions between TBP and AD1+AD2. Binding reactions contained GST-fusion proteins (TBP or HSF1 AD1+2) immobilized on glutathione-Sepharose beads and equal amounts of the ligand proteins present in crude extracts from E. coli or in a nuclear extract from transformed HeLa cells. The ligand proteins in the extracts were tagged with the T7 epitope at the N-terminus. The shaded region corresponds to TBP sequences interacting with HSF1. R1 and R2 indicate repeated sequences of the conserved core. (B) Western blot of AD1+2 in E. coli extract bound to immobilized GST-TBP fusion proteins corresponding to the TBP deletions depicted in panel A. (C) Western blot of TBP deletions bound to GST-AD1+2. TBP deletions from E. coli lysate were used in binding reactions with immobilized GST-AD1+2 fusion protein. (D) Western blot of TBP deletions bound to GST-AD1+2. TBP deletions from transformed HeLa cell lysates were used to interact with GST-AD1+2 fusion protein and were detected with anti-T7 tag antibody. The bars indicate the expected positions of bands representing deleted TBP proteins. Lane numbers correspond to TBP constructs in panel A. Lane C in all panels represents the negative control showing the amount of nonspecific interaction between full-length TBP (ligand) and immobilized GST
