Fig 8.
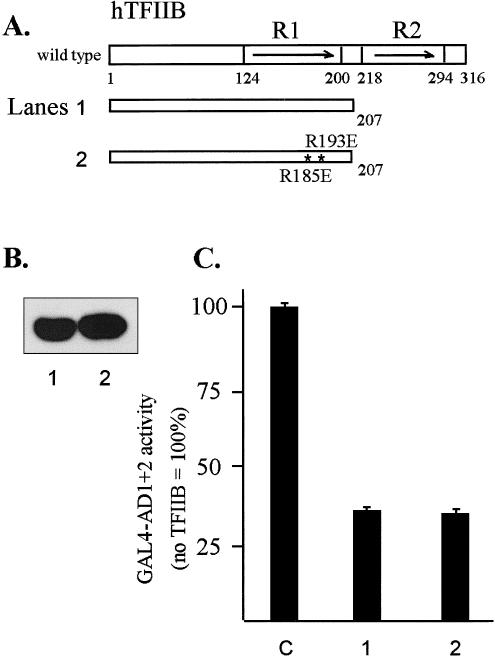
In vivo interactions between AD1+2 and TFIIB analyzed by transcriptional interference assays. (A) Diagram of TFIIB and mutant proteins. The asterisks indicate 2 point mutations in E1 helix of hTFIIB: R185 to E185 and R193 to E193. (B) Western blot of T7-tagged TFIIB mutants transiently expressed in HeLa cells and detected with anti-T7 tag antibody. (C) Inhibition of GAL4-AD1+2 activity by the wild-type and mutated TFIIB1-207 deletion. In transformations, the first effector was the GAL4-AD1+2 fusion in vector pNG-SB, and the second effector was the indicated TFIIB deletion fragment with the T7-epitope tag and nuclear localization signal in vector pT7-NLS. The luciferase reporter plasmid was pG5luc, and DNA from pCI-neo served as the empty-vector control (lane C). Cotransfected DNAs were as follows: 0.3 μg of GAL4-AD1+2, 3 μg of TFIIB mutant, 2 μg of luciferase reporter (pG5luc), and 0.5 μg of growth hormone reporter (pXGH5). Luciferase activity from triplicate assays was normalized using human growth hormone expression
