Fig 4.
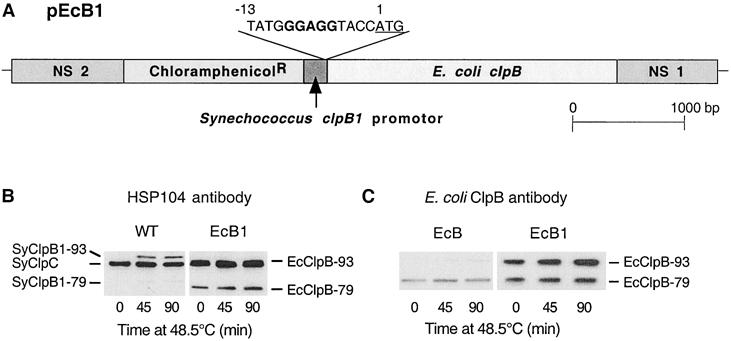
Increased synthesis of EcClpB-93 in Synechococcus ΔclpB1 mutant. (A) Structural representation of the second construct pEcB1 used to increase the amount of EcClpB-93 protein synthesized in the Synechococcus ΔclpB1 strain. The pEcB1 was made as described for pEcB in Figure 1A, except for the altered RBS (bold) upstream of the ATG start codon (underlined) in base position 1. (B,C) Induction of ClpB proteins in wild-type (WT) Synechococcus and the complementation strains EcB and EcB1. All 3 strains were shifted from 37 to 48.5°C for 90 minutes, and cellular proteins were isolated at selected times and then separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis on the basis of equal Chl content. (B) Immunoblot detection of SyClpC, SyClpB1–93, and –79 in WT, and SyClpC and EcClpB-93 and -79 in EcB1 using the yeast Hsp104 antibody. (C) Immunoblot detection of EcClpB proteins in the EcB and EcB1 strains using a specific polyclonal antibody. Results are representative of 3 replicates
