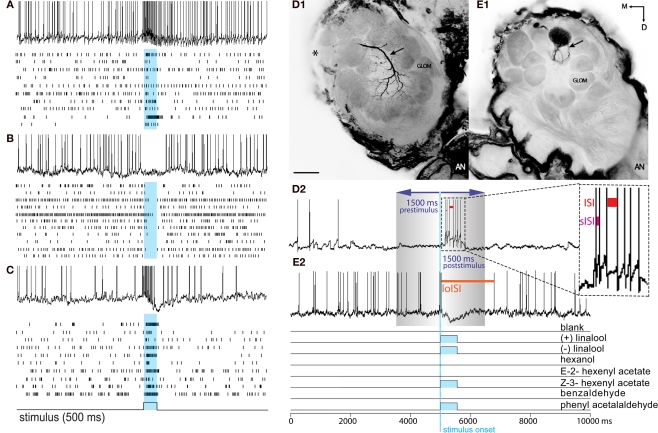
Figure 1.
Response profiles of single AL neurons to an complex odor mixture. Left panel: (A–C) The three basic Manduca response types (A) Excitatory. (B) Inhibitory. (C) Biphasic. Each block shows one example of an intracellular recording trace and complete raster plots of action potentials for all analyzed cells of the dataset in response to plant odor mixtures. Blue squares and vertical bars indicate the 500 ms odor stimulus period. Right panel: Example of two common morphological types of AL neurons in the female Manduca sexta brain responding to an identical mixture of four components. Both neurons innervate the right antennal lobe. (D1) Typical local interneuron (LN) with a broad symmetrical aborization profile, branching in the vast majority of glomeruli with soma situated in the lateral cell cluster (not visual in the confocal plane but indicated by asterisk); LN neurites are restricted to the antennal lobe; excitatory response profile (D2). (E1) Uniglomerular projection neuron exhibiting dense dendritic arborization occupying one single ordinary glomerulus; soma antero-ventral, axon innervating the mushroom bodies via the inner antennocerebral tract (IACT, compare Figure 2E,F); inhibitory response profile (E2). Pictures were obtained by confocal microscopy of two separate whole mount brain preparations; anterior inverted projection view of picture stack [(D) = average of 50 pictures; (E) = 11]; M, medial; D, dorsal; AN, antennal nerve; GLOM, glomerulus; Scale bar, 100μm. (D2,E2) To determine response frequencies the number of spikes was counted 1.5 s before (prestimulus period) and 1.5 s after stimulus onset (poststimulus period; stimulus onset: blue, vertical dotted line). To determine latency, interspike intervals (ISIs) were calculated between successive spikes (ISI: red bar; shortest ISI “sISI”: magenta bar; longest ISI “loISI”: orange bar).